Glyphs.app Python Scripting API Documentation¶
This is the documentation for the Python Scripting API for Glyphs.app (glyphsapp.com)
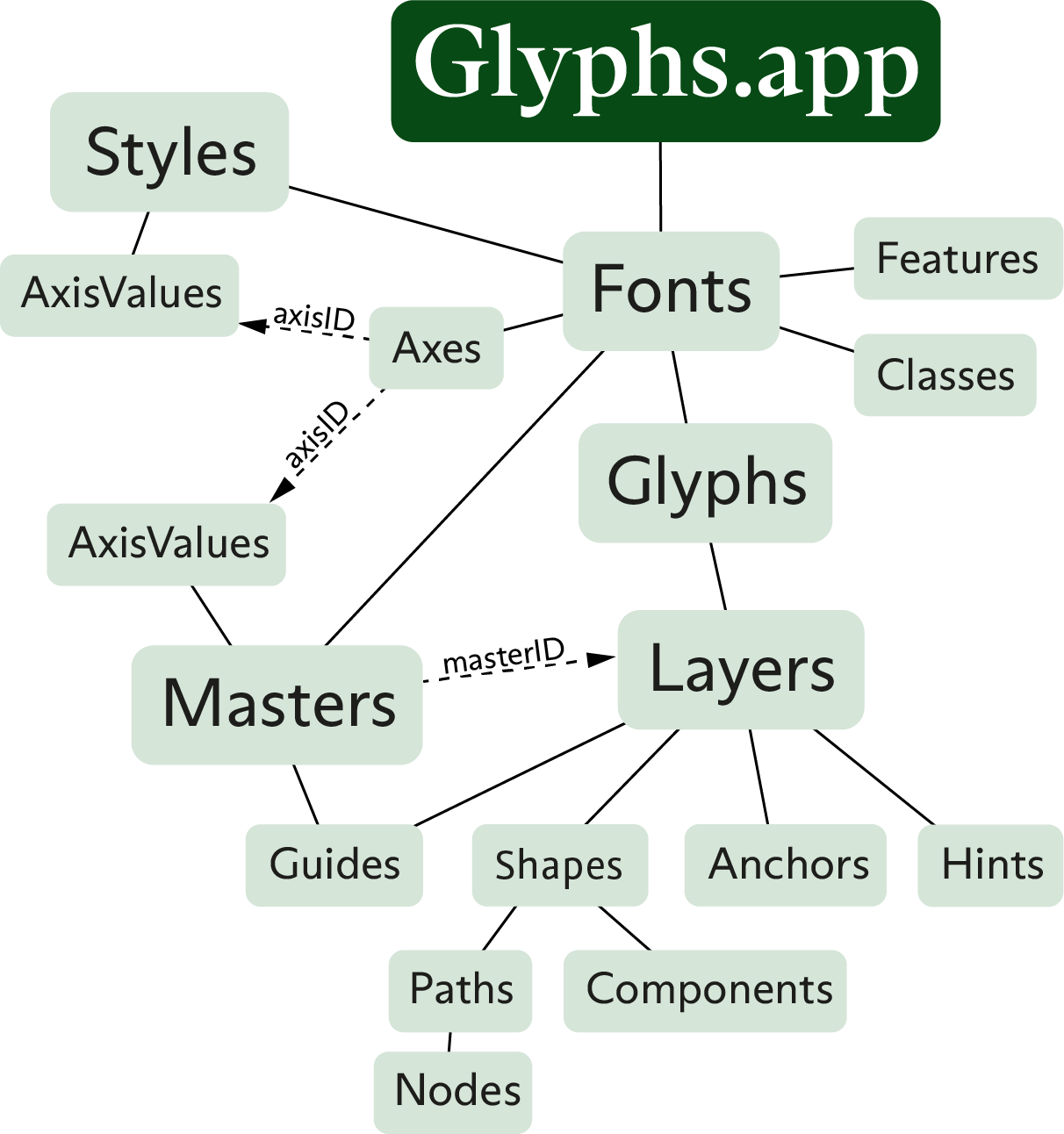
About this Document¶
This document covers all methods that are implemented in the Python wrapper. There are many more functions and objects available via the PyObjC bridge. For more details, please have a look at the Core part of the documentation.
Changes in the API¶
These changes could possibly break your code, so you need to keep track of them. Please see GSApplication.versionNumber for how to check for the app version in your code. Really, read it. There’s a catch.
GSApplication¶
The mothership. Everything starts here.
print(Glyphs)<Glyphs.app>- class GSApplication¶
- Properties
Functions
Properties
- currentDocument¶
The active
GSDocumentobject or None.- Type:
# topmost open document document = Glyphs.currentDocument
- documents¶
An array of open
GSDocumentobjects.- Type:
list
- fonts¶
Be aware that the order is defined by last used font. Append and extend generally don’t insert at the end of the list.
- Type:
list
# access all open fonts for font in Glyphs.fonts: print(font.familyName) # add a font font = GSFont() font.familyName = "My New Font" Glyphs.fonts.append(font)
- reporters¶
List of available reporter plug-ins (same as bottom section in the ‘View’ menu). These are the actual objects. You can get hold of their names using object.__class__.__name__.
Also see
GSApplication.activateReporter()andGSApplication.deactivateReporter()methods below to activate/deactivate them.- Type:
list
# List of all reporter plug-ins print(Glyphs.reporters) # Individual plug-in class names for reporter in Glyphs.reporters: print(reporter.__class__.__name__) # Activate a plugin Glyphs.activateReporter(Glyphs.reporters[0]) # by object Glyphs.activateReporter('GlyphsMasterCompatibility') # by class name
- activeReporters¶
List of activated reporter plug-ins.
- Type:
list
# Activate a plugin Glyphs.activateReporter(Glyphs.reporters[0]) # list of currently active reporter plug-ins activeReporters = Glyphs.activeReporters
- filters¶
List of available filters (same as ‘Filter’ menu). These are the actual objects.
Below sample code shows how to get hold of a particular filter and use it. You invoke it using the processFont_withArguments_() function for old plugins, or the filter() function for newer plugins. As arguments you use the list obtained by clicking on ‘Copy Custom Parameter’ button in the filter’s dialog (gear icon) and convert it to a list. In the include option you can supply a comma-separated list of glyph names.
- Type:
list
# Helper function to get filter by its class name def filterForName(name): for filter in Glyphs.filters: if filter.__class__.__name__ == name: return filter # Get the filter offsetCurveFilter = filterForName('GlyphsFilterOffsetCurve') # Run the filter (old plugins) # The arguments came from the 'Copy Custom Parameter' as: # Filter = "GlyphsFilterOffsetCurve;10;10;1;0.5;" offsetCurveFilter.processFont_withArguments_(font, ['GlyphsFilterOffsetCurve', '10', '10', '1', '0.5', 'include:%s' % glyph.name]) # If the plugin were a new filter, the same call would look like this: # (run on a specific layer, not the first layer glyphs in the include-list) # The arguments list is a dictionary with either incrementing integers as keys or names (as per 'Copy Custom Parameter' list) offsetCurveFilter.filter(layer, False, {0: 10, 1: 10, 2: 1, 3: 0.5})
Added in version After: 2.4.2
- defaults¶
A dict like object for storing preferences. You can get and set key-value pairs.
Please be careful with your keys. Use a prefix that uses the reverse domain name. e.g.
com.MyName.foo.bar.- Type:
dict
# Check for whether or not a preference exists if "com.MyName.foo.bar" in Glyphs.defaults: # do stuff # Get and set values value = Glyphs.defaults["com.MyName.foo.bar"] Glyphs.defaults["com.MyName.foo.bar"] = newValue # Remove value # This will restore the default value del Glyphs.defaults["com.MyName.foo.bar"]
- boolDefaults¶
Access to default settings cast to a bool.
- Type:
bool
if Glyphs.boolDefaults["com.MyName.foo.bar"]: print('"com.MyName.foo.bar" is set')
- scriptAbbreviations¶
A dictionary with script name to tag mapping, e.g., ‘arabic’: ‘arab’ or ‘devanagari’: ‘dev2’
- Type:
dict
- scriptSuffixes¶
A dictionary with glyphs name suffixes for scripts and their respective script names, e.g., ‘cy’: ‘cyrillic’
- Type:
dict
- languageScripts¶
A dictionary with language tag to script tag mapping, e.g., ‘ENG’: ‘latn’
- Type:
dict
- languageData¶
A list of dictionaries with more detailed language informations.
- Type:
list
- unicodeRanges¶
Names of unicode ranges.
- Type:
list
- editViewWidth¶
Width of glyph Edit view. Corresponds to the “Width of editor” setting from the Preferences.
- Type:
int
- handleSize¶
Size of Bezier handles in Glyph Edit view. Possible value are 0–2. Corresponds to the ‘Handle size’ setting from the Preferences.
To use the handle size for drawing in reporter plugins, you need to convert the handle size to a point size, and divide by the view’s scale factor. See example below.
- Type:
int
# Calculate handle size handSizeInPoints = 5 + Glyphs.handleSize * 2.5 # (= 5.0 or 7.5 or 10.0) scaleCorrectedHandleSize = handSizeInPoints / Glyphs.font.currentTab.scale # Draw point in size of handles point = NSPoint(100, 100) NSColor.redColor.set() rect = NSRect((point.x - scaleCorrectedHandleSize * 0.5, point.y - scaleCorrectedHandleSize * 0.5), (scaleCorrectedHandleSize, scaleCorrectedHandleSize)) bezierPath = NSBezierPath.bezierPathWithOvalInRect_(rect) bezierPath.fill()
- versionString¶
String containing Glyph.app’s version number. May contain letters also, like ‘2.3b’. To check for a specific version, use
Glyphs.versionNumberbelow.- Type:
str
- versionNumber¶
Glyph.app’s version number. Use this to check for version in your code.
- Type:
float
- buildNumber¶
Glyph.app’s build number.
Especially if you’re using preview builds, this number may be more important to you than the version number. The build number increases with every released build and is the most significant evidence of new Glyphs versions, while the version number is set arbitrarily and stays the same until the next stable release.
- Type:
float
Add menu items to Glyphs’ main menus.
Following constants for accessing the menus are defined:
APP_MENU,FILE_MENU,EDIT_MENU,GLYPH_MENU,PATH_MENU,FILTER_MENU,VIEW_MENU,SCRIPT_MENU,WINDOW_MENU,HELP_MENUdef doStuff(sender): # do stuff newMenuItem = NSMenuItem('My menu title', doStuff) Glyphs.menu[EDIT_MENU].append(newMenuItem)
Functions
- open(Path[, showInterface=True])¶
Opens a document
- Parameters:
Path (str) – The path where the document is located.
showInterface (bool) – If a document window should be opened. Default: True
- Returns:
The opened document object or None.
- Return type:
- showMacroWindow()¶
Opens the macro window
- clearLog()¶
Deletes the content of the console in the macro window
- showGlyphInfoPanelWithSearchString(String)¶
Shows the Glyph Info window with a preset search string
- Parameters:
String – The search term
- glyphInfoForName(name[, font=None])¶
Generates
GSGlyphInfoobject for a given glyph name.- Parameters:
name – Glyph name
font – if you add a font, and the font has a local glyph info, it will be used instead of the global info data.
- Returns:
- glyphInfoForUnicode(Unicode[, font=None])¶
Generates
GSGlyphInfoobject for a given hex unicode.- Parameters:
Unicode – Hex unicode
font – if you add a font, and the font has a local glyph info, it will be used instead of the global info data.
- Returns:
- niceGlyphName(name[, font=None])¶
Converts glyph name to nice, human-readable glyph name (e.g. afii10017 or uni0410 to A-cy)
- Parameters:
name – glyph name
font – if you add a font, and the font has a local glyph info, it will be used instead of the global info data.
- Returns:
string
- productionGlyphName(name[, font=None])¶
Converts glyph name to production glyph name (e.g. afii10017 or A-cy to uni0410)
- Parameters:
name – glyph name
font – if you add a font, and the font has a local glyph info, it will be used instead of the global info data.
- Returns:
string
- ligatureComponents(String[, font=None])¶
If defined as a ligature in the glyph database, this function returns a list of glyph names that this ligature could be composed of.
- Parameters:
string – glyph name
font – if you add a font, and the font has a local glyph info, it will be used instead of the global info data.
- Return type:
list
print(Glyphs.ligatureComponents('allah-ar')) >> ( "alef-ar", "lam-ar.init", "lam-ar.medi", "heh-ar.fina" )
- addCallback(function, hook)¶
Add a user-defined function to the glyph window’s drawing operations, in the foreground and background for the active glyph as well as in the inactive glyphs.
The function names are used to add/remove the functions to the hooks, so make sure to use unique function names.
Your function needs to accept two values: layer which will contain the respective
GSLayerobject of the layer we’re dealing with and info which is a dictionary and contains the value Scale (for the moment).For the defined keys see Callback Keys
def drawGlyphIntoBackground(layer, info): # Due to internal Glyphs.app structure, we need to catch and print exceptions # of these callback functions with try/except like so: try: # Your drawing code here NSColor.redColor().set() layer.bezierPath.fill() # Error. Print exception. except: import traceback print(traceback.format_exc()) # add your function to the hook Glyphs.addCallback(drawGlyphIntoBackground, DRAWBACKGROUND)
- removeCallback(function)¶
Remove the function you’ve previously added.
# remove your function from the hook Glyphs.removeCallback(drawGlyphIntoBackground)
- redraw()¶
Redraws all Edit views and Preview views.
- showNotification(title, message)¶
Shows the user a notification in Mac’s Notification Center.
Glyphs.showNotification('Export fonts', 'The export of the fonts was successful.')
- localize(localization)¶
Return a string in the language of Glyphs.app’s UI locale, which must be supplied as a dictionary using language codes as keys.
The argument is a dictionary in the languageCode: translatedString format.
You don’t need to supply strings in all languages that the Glyphs.app UI supports. A subset will do. Just make sure that you add at least an English string to default to next to all your other translated strings. Also don’t forget to mark strings as unicode strings (
'öäüß') when they contain non-ASCII content for proper encoding, and add a # encoding: utf-8 to the top of all your .py files.Tip: You can find Glyphs’ localized languages here
Glyphs.defaults["AppleLanguages"].print(Glyphs.localize({ 'en': 'Hello World', 'de': 'Hallöle Welt', 'fr': 'Bonjour tout le monde', 'es': 'Hola Mundo', })) # Given that your Mac’s system language is set to German # and Glyphs.app UI is set to use localization (change in app settings), # it will print: >> Hallöle Welt
- activateReporter(reporter)¶
Activate a reporter plug-in by its object (see Glyphs.reporters) or class name.
Glyphs.activateReporter('GlyphsMasterCompatibility')
- deactivateReporter(reporter)¶
Deactivate a reporter plug-in by its object (see Glyphs.reporters) or class name.
Glyphs.deactivateReporter('GlyphsMasterCompatibility')
GSDocument¶
The document class
GSFont¶
Implementation of the font object. This object is host to the masters used for interpolation. Even when no interpolation is involved, for the sake of object model consistency there will still be one master and one instance representing a single font.
Also, the glyphs are attached to the Font object right here, not one level down to the masters. The different masters’ glyphs are available as layers attached to the glyph objects which are attached here.
- class GSFont(([path]))¶
- Parameters:
path – the path to a glyphs file
Properties
Functions
Properties
- parent¶
Returns the internal NSDocument document. Read-only.
- Type:
NSDocument
- masters¶
Collection of
GSFontMasterobjects.- Type:
list
- instances¶
Collection of
GSInstanceobjects.for instance in font.instances: print(instance) # to add a new instance instance = GSInstance() instance.name = "Some Instance" font.instances.append(instance) # to delete an instances del font.instances[0] font.instances.remove(someInstance)
- Type:
list
- axes¶
Collection of
GSAxis:for axis in font.axes: print(axis) # to add a new axis axis = GSAxis() axis.name = "Some custom Axis" axis.axisTag = "SCAX" font.axes.append(axis) # to delete an axis del font.axes[0] font.axes.remove(someAxis)
- Type:
list
Added in version 2.5.
Changed in version 3.
- properties¶
Holds the fonts info properties. Can be instances of
GSFontInfoValueSingleandGSFontInfoValueLocalized.The localized values use language tags defined in the middle column of Language System Tags table: <https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/typography/opentype/spec/languagetags>.
The names are listed in the constants: Info Property Keys
# To access the default value: font.properties["versionString"] font.properties["versionString"] = "version 1.0" # To access specific languages: font.properties.getProperty(GSPropertyNameDesignersKey, "DEU") font.properties.setProperty(GSPropertyNameDesignersKey, "SomeName", "DEU")
- Type:
list
Added in version 3.
- metrics¶
a list of all
GSMetricobjects.- Type:
list
# to add a new metric metric = GSMetric(GSMetricsTypexHeight) font.metrics.append(metric) metricValue = master.metricValues[metric.id] metricValue.position = 543 metricValue.overshoot = 17
- stems¶
The stems. A list of
GSMetricobjects. For each metric, there is a metricsValue in the masters, linked by the id.- Type:
list, dict
font.stems[0].horizontal = False # add a stem stem = GSMetric() stem.horizontal = False # or True stem.name = "Some Name" font.stems.append(stem) master.stems[stem.name] = 123
- numbers¶
The numbers. A list of
GSMetricobjects. For each number, there is a metricsValue in the masters, linked by the id.- Type:
list, dict
print(font.numbers[0].name) # add a number number = GSMetric() number.horizontal = False # or True number.name = "Some Name" font.numbers.append(number) master.numbers[number.name] = 123
- glyphs¶
Collection of
GSGlyphobjects. Returns a list, but you may also call glyphs using index or glyph name or character as key.- Type:
list, dict
# Access all glyphs for glyph in font.glyphs: print(glyph) >> <GSGlyph "A" with 4 layers> >> <GSGlyph "B" with 4 layers> >> <GSGlyph "C" with 4 layers> ... # Access one glyph print(font.glyphs['A']) >> <GSGlyph "A" with 4 layers> # Access a glyph by character (new in v2.4.1) print(font.glyphs['Ư']) >> <GSGlyph "Uhorn" with 4 layers> # Access a glyph by unicode (new in v2.4.1) print(font.glyphs['01AF']) >> <GSGlyph "Uhorn" with 4 layers> # Access a glyph by index print(font.glyphs[145]) >> <GSGlyph "Uhorn" with 4 layers> # Add a glyph font.glyphs.append(GSGlyph('adieresis')) # Duplicate a glyph under a different name newGlyph = font.glyphs['A'].copy() newGlyph.name = 'A.alt' font.glyphs.append(newGlyph) # Delete a glyph del font.glyphs['A.alt']
- characterForGlyph(glyph)¶
The (internal) character that is used in the edit view. It the glyph has a unicode, that is used, otherwise a temporary code is assigned. That can change over time, so don’t rely on it. This is mostly useful for constructing a string for see
tab.textAdded in version 3.1.
- classes¶
Collection of
GSClassobjects, representing OpenType glyph classes.- Type:
list
# add a class font.classes.append(GSClass('uppercaseLetters', 'A B C D E')) # access all classes for class in font.classes: print(class.name) # access one class print(font.classes['uppercaseLetters'].code) # delete a class del font.classes['uppercaseLetters']
- features¶
Collection of
GSFeatureobjects, representing OpenType features.- Type:
list
# add a feature font.features.append(GSFeature('liga', 'sub f i by fi;')) # access all features for feature in font.features: print(feature.code) # access one feature print(font.features['liga'].code) # delete a feature del font.features['liga']
- featurePrefixes¶
Collection of
GSFeaturePrefixobjects, containing stuff that needs to be outside of the OpenType features.- Type:
list
# add a prefix font.featurePrefixes.append(GSFeaturePrefix('LanguageSystems', 'languagesystem DFLT dflt;')) # access all prefixes for prefix in font.featurePrefixes: print(prefix.code) # access one prefix print(font.featurePrefixes['LanguageSystems'].code) # delete del font.featurePrefixes['LanguageSystems']
- copyright¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
- copyrights¶
This accesses all localized copyright values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.copyrights["ENG"] = "All rights reserved"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- license¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- licenses¶
This accesses all localized license values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.licenses["ENG"] = "This font may be installed on all of your machines and printers, but you may not sell or give these fonts to anyone else."
Added in version 3.0.3.
- compatibleFullName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- compatibleFullNames¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.compatibleFullNames["ENG"] = "MyFont Condensed Bold"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- sampleText¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- sampleTexts¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.sampleTexts["ENG"] = "This is my sample text"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- description¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- descriptions¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.descriptions["ENG"] = "This is my description"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- designer¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
- designers¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.designers["ENG"] = "John Smith"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- trademark¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- trademarks¶
This accesses all localized trademark values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.trademarks["ENG"] = "ThisFont is a trademark by MyFoundry.com"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- designerURL¶
- Type:
str
- manufacturer¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSFont.properties- Type:
str
- manufacturers¶
This accesses all localized manufacturer values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.manufacturers["ENG"] = "My English Corporation"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- manufacturerURL¶
- Type:
str
- versionMajor¶
- Type:
int
- versionMinor¶
- Type:
int
- date¶
- Type:
datetime.datetime
print(font.date) >> 2015-06-08 09:39:05 # set date to now font.date = datetime.datetime.now() # using NSDate font.date = NSDate.date() # or in seconds since Epoch font.date = time.time()
- familyName¶
Family name of the typeface.
- Type:
str
- familyNames¶
This accesses all localized family name values. For details
GSFont.properties- Type:
dict
font.familyNames["ENG"] = "MyFamilyName"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- upm¶
Units per Em
- Type:
int
- note¶
- Type:
str
- kerning¶
Kerning for LTR writing A multi-level dictionary. The first level’s key is the
GSFontMaster.id(each master has its own kerning), the second level’s key is theGSGlyph.idor class id (@MMK_L_XX) of the first glyph, the third level’s key is a glyph id or class id (@MMK_R_XX) for the second glyph. The values are the actual kerning values.To set a value, it is better to use the method
GSFont.setKerningForPair(). This ensures a better data integrity (and is faster).- Type:
dict
- kerningRTL¶
Kerning for RTL writing A multi-level dictionary. The first level’s key is the
GSFontMaster.id(each master has its own kerning), the second level’s key is theGSGlyph.idor class id (@MMK_L_XX) of the first glyph, the third level’s key is a glyph id or class id (@MMK_R_XX) for the second glyph. The values are the actual kerning values.To set a value, it is better to use the method
GSFont.setKerningForPair(). This ensures a better data integrity (and is faster).- Type:
dict
- kerningVertical¶
Kerning for vertical writing A multi-level dictionary. The first level’s key is the
GSFontMaster.id(each master has its own kerning), the second level’s key is theGSGlyph.idor class id (@MMK_L_XX) of the first glyph, the third level’s key is a glyph id or class id (@MMK_R_XX) for the second glyph. The values are the actual kerning values.To set a value, it is better to use the method
GSFont.setKerningForPair(). This ensures a better data integrity (and is faster).- Type:
dict
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value font.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del font.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use layer.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- disablesNiceNames¶
Corresponds to the “Don’t use nice names” setting from the Font Info dialog.
- Type:
bool
- customParameters¶
The custom parameters. List of
GSCustomParameterobjects. You can access them by name or by index.- Type:
list, dict
# access all parameters for parameter in font.customParameters: print(parameter) # set a parameter font.customParameters['glyphOrder'] = ["a", "b", "c"] # add multiple parameters: parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "1 1;"font name") font.customParameters.append(parameter) parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "2 1;"style name") font.customParameters.append(parameter) # delete a parameter del font.customParameters['glyphOrder']
- grid¶
Corresponds to the “Grid spacing” setting from the Info dialog.
- Type:
int
- gridSubDivision¶
Corresponds to the “Grid sub divisions” setting from the Info dialog.
- Type:
int
- gridLength¶
Ready calculated size of grid for rounding purposes. Result of division of grid with gridSubDivisions.
- Type:
float (readonly)
- disablesAutomaticAlignment¶
- Type:
bool
- keyboardIncrement¶
Distance of movement by arrow keys. Default:1
- Type:
float
- keyboardIncrementBig¶
Distance of movement by arrow plus Shift key. Default:10
- Type:
float
Added in version 3.0.
- keyboardIncrementHuge¶
Distance of movement by arrow plus Command key. Default:100
- Type:
float
Added in version 3.0.
- snapToObjects¶
disable snapping to nodes and background
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.0.1.
- previewRemoveOverlap¶
disable preview remove overlap
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.0.1.
- selection¶
Returns a list of all selected glyphs in the Font View.
- Type:
list
- selectedLayers¶
Returns a list of all selected layers in the active tab.
If a glyph is being edited, it will be the only glyph returned in this list. Otherwise the list will contain all glyphs selected with the Text tool.
- Type:
list
- selectedFontMaster¶
Returns the active master (selected in the toolbar).
- Type:
- masterIndex¶
Returns the index of the active master (selected in the toolbar).
- Type:
int
- currentText¶
The text of the current Edit view.
Unencoded and none ASCII glyphs will use a slash and the glyph name. (e.g: /a.sc). Setting unicode strings works.
- Type:
str
- tabs¶
List of open Edit view tabs in UI, as list of
GSEditViewControllerobjects.- Type:
list
# open new tab with text font.newTab('hello') # access all tabs for tab in font.tabs: print(tab) # close last tab font.tabs[-1].close()
- fontView¶
- Type:
GSFontViewController
- currentTab¶
Active Edit view tab.
- Type:
- filepath¶
On-disk location of GSFont object.
- Type:
str
- tool¶
Name of tool selected in toolbar.
For available names including third-party plug-ins that come in the form of selectable tools, see GSFont.tools below.
- Type:
str
font.tool = 'SelectTool' # Built-in tool font.tool = 'GlyphsAppSpeedPunkTool' # Third party plug-in
- tools¶
Returns a list of available tool names, including third-party plug-ins.
- Type:
list, str
- appVersion¶
Returns the version that the file was last saved
Added in version 2.5.
- formatVersion¶
The file-format the font should be written. possible values are ‘2’ and ‘3’. You can use File Format Versions
- Type:
int
Added in version 3.
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the font
- save([path=None, formatVersion=3, makeCopy=False])¶
Saves the font.
If no path is given, it saves to the existing location.
- Parameters:
path (str) – (Optional) file path including filename and suffix. When the font is loaded directly (GSFont(path)), the path argument is required.
formatVersion (int) – The format of the file. Requires makeCopy=True
makeCopy (bool) – saves a new file without changing the documents file paths. So it always need a path argument
- close([ignoreChanges=True])¶
Closes the font.
- Parameters:
ignoreChanges (bool) – Optional. Ignore changes to the font upon closing
- disableUpdateInterface()¶
Disables interface updates and thus speeds up glyph processing. Call this before you do big changes to the font, or to its glyphs. Make sure that you call
font.enableUpdateInterface()when you are done.
- enableUpdateInterface()¶
This re-enables the interface update. Only makes sense to call if you have disabled it earlier.
- show()¶
Makes font visible in the application, either by bringing an already open font window to the front or by appending a formerly invisible font object (such as the result of a copy() operation) as a window to the application.
Added in version 2.4.1.
- kerningForPair(fontMasterId, leftKey, rightKey[, direction=LTR])¶
This returns the kerning value for the two specified glyphs (leftKey or rightKey is the glyph name) or a kerning group key (@MMK_X_XX).
- Parameters:
fontMasterId (str) – The id of the FontMaster
leftKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
rightKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
direction (int) – optional writing direction (see Constants; ‘LTR’ (0) or ‘RTLTTB’). Default is LTR.
- Returns:
The kerning value
- Return type:
float
# print(kerning between w and e for currently selected master) font.kerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, 'w', 'e') >> -15.0 # print(kerning between group T and group A for currently selected master) # ('L' = left side of the pair and 'R' = left side of the pair) font.kerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, '@MMK_L_T', '@MMK_R_A') >> -75.0 # in the same font, kerning between T and A would be zero, because they use group kerning instead. font.kerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, 'T', 'A') >> None
- setKerningForPair(fontMasterId, leftKey, rightKey, value[, direction=GSLTR])¶
This sets the kerning for the two specified glyphs (leftKey or rightKey is the glyph name) or a kerning group key (@MMK_X_XX).
- Parameters:
fontMasterId (str) – The id of the FontMaster
leftKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
rightKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
value (float) – kerning value
direction (str) – optional writing direction (see Constants). Default is GSLTR.
# set kerning for group T and group A for currently selected master # ('L' = left side of the pair and 'R' = left side of the pair) font.setKerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, '@MMK_L_T', '@MMK_R_A', -75)
- removeKerningForPair(fontMasterId, leftKey, rightKey, direction=GSLTR)¶
Removes the kerning for the two specified glyphs (LeftKey or RightKey is the glyph name) or a kerning group key (@MMK_X_XX).
- Parameters:
FontMasterId (str) – The id of the FontMaster
leftKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
rightKey (str) – either a glyph name or a class name
direction (int) – optional writing direction (see Constants; ‘GSLTR’ (0) or ‘GSVertical’). Default is GSLTR. (added in 2.6.6)
# remove kerning for group T and group A for all masters # ('L' = left side of the pair and 'R' = left side of the pair) for master in font.masters: font.removeKerningForPair(master.id, '@MMK_L_T', '@MMK_R_A')
- newTab([tabText])¶
Opens a new tab in the current document window, optionally with text, and return that tab object
- Parameters:
tabText – Text or glyph names escaped with ‘/’ OR list of layers
# open new tab tab = font.newTab('abcdef') print(tab) # or tab = font.newTab([layer1, layer2]) print(tab)
- updateFeatures()¶
Updates all OpenType features and classes at once, including generating necessary new features and classes. Equivalent to the “Update” button in the features panel. This already includes the compilation of the features (see
font.compileFeatures()).Added in version 2.4.
- compileFeatures()¶
Compiles the features, thus making the new feature code functionally available in the editor. Equivalent to the “Compile” button in the features panel.
Added in version 2.5.
- export([format, instances, fontPath, autoHint, removeOverlap, useSubroutines, useProductionNames, containers, decomposeSmartStuff)¶
exports the font
GSAxis¶
Implementation of the axis object.
- class GSAxis¶
Properties
Properties
- name¶
The name of the axis
- Type:
str
- axisTag¶
The axisTag. this is a four letter string. see OpenType Design-Variation Axis Tag Registry.
- Type:
str
- id¶
The id to link the values in the masters
- Type:
str
If the axis should be shown to the user
- Type:
bool
GSMetric¶
Implementation of the metric object. It is used to link the metrics and stems in the masters.
- class GSMetric¶
Properties
Properties
- font¶
Reference to the
GSFontobject that contains the metric. Normally that is set by the app.- Type:
- name¶
The name of the metric or stem
- Type:
str
- id¶
The id to link the values in the masters
- Type:
str
- title¶
The title as shown in the UI. It is readonly as it is computed by the name, type and filter.
- Type:
str
- type¶
The metrics type
- Type:
int
- filter¶
A filter to limit the scope of the metric.
- Type:
NSPredicate
- horizontal¶
This is used for stem metrics. so only use this for font.stems
- Type:
bool
GSFontMaster¶
Implementation of the master object. This corresponds with the “Masters” pane in the Font Info. In Glyphs.app, the glyphs of each master are reachable not here, but as layers attached to the glyphs attached to the font object. See the infographic on top for better understanding.
- class GSFontMaster¶
Functions
Properties
- id¶
Used to identify
Layersin the Glyphsee
GSGlyph.layers- Type:
str
# ID of first master print(font.masters[0].id) >> 3B85FBE0-2D2B-4203-8F3D-7112D42D745E # use this master to access the glyph’s corresponding layer print(glyph.layers[font.masters[0].id]) >> <GSLayer "Light" (A)>
- font¶
Reference to the
GSFontobject that contains the master. Normally that is set by the app, only if the instance is not actually added to the font, then set this manually.- Type:
Added in version 2.5.2.
- name¶
The human-readable identification of the master, e.g., “Bold Condensed”.
- Type:
str
- iconName¶
The name of the icon
- Type:
str
- axes¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis master.axes[2] = 12 # setting all values at once master.axes = [100, 12, 3.5]
Added in version 2.5.2.
Deprecated since version 3.2.
- internalAxesValues¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis master.internalAxesValues[2] = 12 # or more precisely master.internalAxesValues[axis.axisId] = 12 # setting all values at once master.internalAxesValues = [100, 12, 3.5]
Added in version 3.2.
- externalAxesValues¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis for the user facing values
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis master.externalAxesValues[2] = 12 # or more precisely master.externalAxesValues[axis.axisId] = 12 # setting all values at once master.externalAxesValues = [100, 12, 3.5]
Added in version 3.2.
- properties¶
Holds the fonts info properties. Can be instances of
GSFontInfoValueSingleandGSFontInfoValueLocalizedThe localized values use language tags defined in the middle column of Language System Tags table: <https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/typography/opentype/spec/languagetags>.
To find specific values, use master.propertyForName_(name) or master.propertyForName_languageTag_(name, languageTag).
- Type:
list
Added in version 3.
- metricValues¶
only there for compatibility. use
GSFontMaster.metricsAdded in version 3.
Deprecated since version 3.2.
- metrics¶
a dict of all
GSMetricValueobjects. Keys are font.metrics[].id- Type:
dict
for metric in Font.metrics: if metric.type == GSMetricsTypexHeight and metric.filter is None: metricValue = master.metrics[metric.id] metricValue.position = 543 metricValue.overshoot = 17
Added in version 3.3.
- ascender¶
This is the default ascender of the master. There might be other values that are for specific glyphs. See
master.metricsandlayer.metrics- Type:
float
- capHeight¶
This is the default capHeight of the master. There might be other values that are for specific glyphs. See
master.metricsandlayer.metrics- Type:
float
- xHeight¶
This is the default xHeight of the master. There might be other values that are for specific glyphs. See
master.metricsandlayer.metrics- Type:
float
- descender¶
This is the default descender of the master. There might be other values that are for specific glyphs. See
master.metricsandlayer.metrics- Type:
float
- italicAngle¶
- Type:
float
- stems¶
The stems. This is a list of numbers.
- Type:
list
font.masters[0].stems = [10, 11, 20] print(master.stems[0]) master.stems[0] = 12 master.stems["stemName"] = 12
- numbers¶
The numbers. This is a list of numbers.
- Type:
list
font.masters[0].numbers = [10, 11, 20] print(master.numbers[0]) master.numbers[0] = 12 master.numbers["numberName"] = 12
Added in version 3.1.
- alignmentZones¶
Collection of
GSAlignmentZoneobjects. Read-only.- Type:
list
- blueValues¶
PS hinting Blue Values calculated from the master’s alignment zones. Read-only.
- Type:
list
- otherBlues¶
PS hinting Other Blues calculated from the master’s alignment zones. Read-only.
- Type:
list
- guides¶
Collection of
GSGuideobjects. These are the font-wide (actually master-wide) red guidelines. For glyph-level guidelines (attached to the layers) seeGSLayer.guides- Type:
list
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key, and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (bool, string, list, dict, numbers, NSData), otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value font.masters[0].userData['rememberToMakeTea'] = True # delete value del font.masters[0].userData['rememberToMakeTea']
- customParameters¶
The custom parameters. List of
GSCustomParameterobjects. You can access them by name or by index.- Type:
list, dict
# access all parameters for parameter in font.masters[0].customParameters: print(parameter) # set a parameter font.masters[0].customParameters['underlinePosition'] = -135 # add multiple parameters: parameter = GSCustomParameter("CJK Guide", 10) font.customParameters.append(parameter) parameter = GSCustomParameter("CJK Guide", 20) font.customParameters.append(parameter) # delete a parameter del font.masters[0].customParameters['underlinePosition']
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the master
GSAlignmentZone¶
Implementation of the alignmentZone object.
There is no distinction between Blue Zones and Other Zones. All negative zones (except the one with position 0) will be exported as Other Zones.
The zone for the baseline should have position 0 (zero) and a negative width.
GSInstance¶
Implementation of the instance object. This corresponds with the “Exports” pane in Font Info.
- class GSInstance¶
Properties
active
Functions
Properties
- exports¶
- Type:
bool
- visible¶
if visible in the preview in edit view
- Type:
bool
- name¶
Name of instance. Corresponds to the “Style Name” field in the font info. This is used for naming the exported fonts.
- Type:
str
- type¶
the type of the instance. Can be either INSTANCETYPESINGLE or INSTANCETYPEVARIABLE.
- Type:
int
- weightClass¶
Weight class, as set in Font Info, as an integer. Values from 1 to 1000 are supported but 100–900 is recommended.
For actual position in interpolation design space, use GSInstance.axes.
- Type:
int
- weightClassName¶
Human readable name corresponding to the value of GSInstance.weightClass. This attribute is read-only.
Can be None if GSInstance.weightClass is not a multiple of 100.
- Type:
str
- widthClass¶
Width class, as set in Font Info, as an integer. Values from 1 to 9 are supported.
For actual position in interpolation design space, use GSInstance.axes.
- Type:
int
- widthClassName¶
Human readable name corresponding to the value of GSInstance.widthClass. This attribute is read-only.
- Type:
str
- axes¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis instance.axes[2] = 12 # setting all values at once instance.axes = [100, 12, 3.5] # make sure that the count of numbers matches the count of axes
Added in version 2.5.2.
Deprecated since version 3.2.
- internalAxesValues¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis instance.internalAxesValues[2] = 12 # or more precisely instance.internalAxesValues[axis.axisId] = 12 # setting all values at once instance.internalAxesValues = [100, 12, 3.5]
Added in version 3.2.
- externalAxesValues¶
List of floats specifying the positions for each axis for the user facing values
- Type:
list
# setting a value for a specific axis instance.externalAxesValues[2] = 12 # or more precisely instance.externalAxesValues[axis.axisId] = 12 # setting all values at once instance.externalAxesValues = [100, 12, 3.5]
Added in version 3.2.
- properties¶
Holds the fonts info properties. Can be instances of
GSFontInfoValueSingleandGSFontInfoValueLocalizedThe localized values use language tags defined in the middle column of Language System Tags table: <https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/typography/opentype/spec/languagetags>.
The names are listed in the constants: Info Property Keys
# To access the default value: instance.properties["versionString"] instance.properties["versionString"] = "version 1.0" # To access specific languages: instance.properties.getProperty(GSPropertyNameDesignersKey, "DEU") instance.properties.setProperty(GSPropertyNameDesignersKey, "SomeName", "DEU")
- Type:
list
Added in version 3.
- isItalic¶
Italic flag for style linking
- Type:
bool
- isBold¶
Bold flag for style linking
- Type:
bool
- linkStyle¶
Linked style
- Type:
str
- preferredFamily¶
preferredFamily
- Type:
str
- windowsFamily¶
windowsFamily
- Type:
str
- windowsStyle¶
This is computed from “isBold” and “isItalic”. Read-only.
- Type:
str
- windowsLinkedToStyle¶
windowsLinkedToStyle. Read-only.
- Type:
str
- fontName¶
fontName (postscriptFontName)
- Type:
str
- fullName¶
fullName (postscriptFullName)
- Type:
str
- compatibleFullName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- compatibleFullNames¶
This accesses all localized compatibleFullNames values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.compatibleFullNames["ENG"] = "MyFont Condensed Bold"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- copyright¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.2.
- copyrights¶
This accesses all localized copyright values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.copyrights["ENG"] = "All rights reserved"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- description¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- descriptions¶
This accesses all localized description values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.descriptions["ENG"] = "This is my description"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- designer¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.2.
- designerURL¶
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.2.
- designers¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.designers["ENG"] = "John Smith"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- familyName¶
familyName
- Type:
str
- familyNames¶
This accesses all localized family name values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.familyNames["ENG"] = "MyFamilyName"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- license¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- licenses¶
This accesses all localized family name values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.licenses["ENG"] = "This font may be installed on all of your machines and printers, but you may not sell or give these fonts to anyone else."
Added in version 3.0.3.
- manufacturer¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.2.
- manufacturers¶
This accesses all localized family name values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.manufacturers["ENG"] = "My English Corporation"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- preferredFamilyName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- preferredFamilyNames¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.preferredFamilyNames["ENG"] = "MyFamilyName"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- preferredSubfamilyName¶
preferredSubfamilyName
- Type:
str
- preferredSubfamilyNames¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.preferredSubfamilyNames["ENG"] = "Regular"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- sampleText¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- sampleTexts¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.sampleTexts["ENG"] = "This is my sample text"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleMapFamilyName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleMapFamilyNames¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.styleMapFamilyNames["ENG"] = "MyFamily Bold"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleMapStyleName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleMapStyleNames¶
This accesses all localized designer values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.styleMapStyleNames["ENG"] = "Bold"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- styleNames¶
This accesses all localized styleName values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.styleNames["ENG"] = "Regular"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- trademark¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- trademarks¶
This accesses all localized trademark values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.trademarks["ENG"] = "ThisFont is a trademark by MyFoundry.com"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- variableStyleName¶
This accesses the default value only. The localizations can be accessed by
GSInstance.properties- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.3.
- variableStyleNames¶
This accesses all localized variableStyleName values. For details
GSInstance.properties- Type:
dict
instance.variableStyleNames["ENG"] = "Roman"
Added in version 3.0.3.
- manufacturerURL¶
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.0.2.
- font¶
Reference to the
GSFontobject that contains the instance. Normally that is set by the app, only if the instance is not actually added to the font, then set this manually.- Type:
Added in version 2.5.1.
- customParameters¶
The custom parameters. List of
GSCustomParameterobjects. You can access them by name or by index.- Type:
list, dict
# access all parameters for parameter in font.instances[0].customParameters: print(parameter) # set a parameter font.instances[0].customParameters['hheaLineGap'] = 10 # add multiple parameters: parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "1 1;"font name") font.customParameters.append(parameter) parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "2 1;"style name") font.customParameters.append(parameter) # delete a parameter del font.instances[0].customParameters['hheaLineGap']
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value instance.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del instance.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use instance.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value instance.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del instance.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- instanceInterpolations¶
A dict that contains the interpolation coefficients for each master. This is automatically updated if you change interpolationWeight, interpolationWidth, interpolationCustom. It contains FontMaster IDs as keys and coefficients for that master as values. Or, you can set it manually if you set manualInterpolation to True. There is no UI for this, so you need to do that with a script.
- Type:
dict
- manualInterpolation¶
Disables automatic calculation of instanceInterpolations This allows manual setting of instanceInterpolations.
- Type:
bool
- interpolatedFontProxy¶
a proxy font that acts similar to a normal font object but only interpolates the glyphs you ask it for.
It is not properly wrapped yet. So you need to use the ObjectiveC methods directly.
- interpolatedFont¶
Returns a ready interpolated
GSFontobject representing this instance. Other than the source object, this interpolated font will contain only one master and one instance.Note: When accessing several properties of such an instance consecutively, it is advisable to create the instance once into a variable and then use that. Otherwise, the instance object will be completely interpolated upon each access. See sample below.
- Type:
# create instance once interpolated = Glyphs.font.instances[0].interpolatedFont # then access it several times print(interpolated.masters) >> (<GSFontMaster "Light" width 100.0 weight 75.0>) print(interpolated.instances) >> (<GSInstance "Web" width 100.0 weight 75.0>)
Functions
- generate([format, fontPath, autoHint, removeOverlap, useSubroutines, useProductionNames, containers, decomposeSmartStuff])¶
Exports the instance. All parameters are optional.
- Parameters:
format (str) – The format of the outlines:
OTForTTF. Default: OTFfontPath (str) – The destination path for the final fonts. If None, it uses the default location set in the export dialog
autoHint (bool) – If auto hinting should be applied. Default: True
removeOverlap (bool) – If overlaps should be removed. Default: True
useSubroutines (bool) – If to use subroutines for CFF. Default: True
useProductionNames (bool) – If to use production names. Default: True
containers (list) – list of container formats. Use any of the following constants:
PLAIN,WOFF,WOFF2. Default: PLAINdecomposeSmartStuff (bool) – If smart components should be decomposed. Default: True
- Returns:
On success, True; on failure, error message.
- Return type:
bool/list
# export all instances as OpenType (.otf) and WOFF2 to user’s font folder exportFolder = '/Users/myself/Library/Fonts' for instance in Glyphs.font.instances: instance.generate(FontPath=exportFolder, Containers=[PLAIN, WOFF2]) Glyphs.showNotification('Export fonts', 'The export of %s was successful.' % (Glyphs.font.familyName))
- lastExportedFilePath¶
Returns a ready interpolated
GSFontobject representing this instance. Other than the source object, this interpolated font will contain only one master and one instance.Note: When accessing several properties of such an instance consecutively, it is advisable to create the instance once into a variable and then use that. Otherwise, the instance object will be completely interpolated upon each access. See sample below.
- Type:
str
# create instance once interpolated = Glyphs.font.instances[0].interpolatedFont # then access it several times print(interpolated.masters) >> (<GSFontMaster "Light" width 100.0 weight 75.0>) print(interpolated.instances) >> (<GSInstance "Web" width 100.0 weight 75.0>)
- addAsMaster()¶
Add this instance as a new master to the font. Identical to “Instance as Master” menu item in the Font Info’s Instances section.
Added in version 2.6.2.
GSCustomParameter¶
Implementation of the Custom Parameter object. It stores a name/value pair.
You can append GSCustomParameter objects for example to GSFont.customParameters, but this way you may end up with duplicates. It is best to access the custom parameters through its dictionary interface like this:
# access all parameters
for parameter in font.customParameters:
print(parameter)
# set a parameter
font.customParameters['trademark'] = 'ThisFont is a trademark by MyFoundry.com'
# add multiple parameters:
parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "1 1;"font name")
font.customParameters.append(parameter)
parameter = GSCustomParameter("Name Table Entry", "2 1;"style name")
font.customParameters.append(parameter)
# delete a parameter
del font.customParameters['trademark']GSClass¶
Implementation of the class object. It is used to store OpenType classes.
For details on how to access them, please look at GSFont.classes
- class GSClass([tag, code])¶
- Parameters:
Properties
- name¶
The class name
- Type:
str
- code¶
A string with space separated glyph names.
- Type:
str
- automatic¶
Define whether this class should be auto-generated when pressing the ‘Update’ button in the Font Info.
- Type:
bool
- active¶
- Type:
bool
Added in version 2.5.
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use class.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value class.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del class.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
GSFeaturePrefix¶
Implementation of the featurePrefix object. It is used to store things that need to be outside of a feature like standalone lookups.
For details on how to access them, please look at GSFont.featurePrefixes
- class GSFeaturePrefix([tag, code])¶
- Parameters:
Properties
- name¶
The FeaturePrefix name
- Type:
str
- code¶
A String containing feature code.
- Type:
str
- automatic¶
Define whether this should be auto-generated when pressing the ‘Update’ button in the Font Info.
- Type:
bool
- active¶
- Type:
bool
Added in version 2.5.
GSFeature¶
Implementation of the feature object. It is used to implement OpenType Features in the Font Info.
For details on how to access them, please look at GSFont.features
- class GSFeature([tag, code])¶
- Parameters:
tag – The feature name
code – The feature code in Adobe FDK syntax
Properties
Functions
Properties
- name¶
The feature name
- Type:
str
- code¶
The Feature code in Adobe FDK syntax.
- Type:
str
- automatic¶
Define whether this feature should be auto-generated when pressing the ‘Update’ button in the Font Info.
- Type:
bool
- notes¶
Some extra text. Is shown in the bottom of the feature window. Contains the stylistic set name parameter
- Type:
str
- active¶
- Type:
bool
Added in version 2.5.
Functions
- update()¶
Calls the automatic feature code generator for this feature. You can use this to update all OpenType features before export.
# first update all features for feature in font.features: if feature.automatic: feature.update() # then export fonts for instance in font.instances: if instance.active: instance.generate()
- labels¶
List of Feature names for stylistic set features
- Type:
list
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use feature.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value feature.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del feature.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
GSGlyph¶
Implementation of the glyph object.
For details on how to access these glyphs, please see GSFont.glyphs
- class GSGlyph([name, autoName=True])¶
- Parameters:
name – The glyph name
autoName – if the name should be converted to nice name
Properties
Functions
Properties
- layers¶
The layers of the glyph, collection of
GSLayerobjects. You can access them either by index or by layer ID, which can be aGSFontMaster.id. The layer IDs are usually a unique string chosen by Glyphs.app and not set manually. They may look like this: 3B85FBE0-2D2B-4203-8F3D-7112D42D745E- Type:
list, dict
# get active layer layer = font.selectedLayers[0] # get glyph of this layer glyph = layer.parent # access all layers of this glyph for layer in glyph.layers: print(layer.name) # access layer of currently selected master of active glyph ... # (also use this to access a specific layer of glyphs selected in the Font View) layer = glyph.layers[font.selectedFontMaster.id] # directly access 'Bold' layer of active glyph for master in font.masters: if master.name == 'Bold': id = master.id break layer = glyph.layers[id] # add a new layer newLayer = GSLayer() newLayer.name = '{125, 100}' # (example for glyph-level intermediate master) # you may set the master ID that this layer will be associated with, otherwise the first master will be used newLayer.associatedMasterId = font.masters[-1].id # attach to last master font.glyphs['a'].layers.append(newLayer) # duplicate a layer under a different name newLayer = font.glyphs['a'].layers[0].copy() newLayer.name = 'Copy of layer' # FYI, this will still be the old layer ID (in case of duplicating) at this point print(newLayer.layerId) font.glyphs['a'].layers.append(newLayer) # FYI, the layer will have been assigned a new layer ID by now, after having been appended print(newLayer.layerId) # replace the second master layer with another layer newLayer = GSLayer() newLayer.layerId = font.masters[1].id # Make sure to sync the master layer ID font.glyphs['a'].layers[font.masters[1].id] = newLayer # delete last layer of glyph # (Also works for master layers. They will be emptied) del font.glyphs['a'].layers[-1] # delete currently active layer del font.glyphs['a'].layers[font.selectedLayers[0].layerId]
- name¶
The name of the glyph. It will be converted to a “nice name” (afii10017 to A-cy) (you can disable this behavior in font info or the app preference)
- Type:
str
- unicode¶
String with the hex Unicode value of glyph, if encoded.
- Type:
str
- unicodes¶
List of Strings‚ with the hex Unicode values of glyph, if encoded.
- Type:
list
- string¶
String representation of glyph, if encoded. This is similar to the string representation that you get when copying glyphs into the clipboard.
- Type:
str
- id¶
An unique identifier for each glyph
- Type:
str
- locked¶
If the glyph is locked TODO
- Type:
bool
- category¶
The category of the glyph. e.g. ‘Letter’, ‘Symbol’ Setting only works if
GSGlyph.storeCategoryis set (see below).- Type:
str
- storeCategory¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.categoryof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
- subCategory¶
The subCategory of the glyph. e.g. ‘Currency’, ‘Math’ Setting it only works if
GSGlyph.storeSubCategoryis set (see below).- Type:
str
- storeSubCategory¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.subCategoryof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
- case¶
e.g: GSUppercase, GSLowercase, GSSmallcaps
- Type:
int
Added in version 3.
- storeCase¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.caseof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.
- direction¶
Writing direction.
- Type:
integer
glyph.direction = GSRTL
Added in version 3.
- storeDirection¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.directionof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.
- script¶
The script of the glyph, e.g., ‘latin’, ‘arabic’. Setting only works if
GSGlyph.storeScriptis set (see below).- Type:
str
- storeScript¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.scriptof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
- productionName¶
The productionName of the glyph. Setting only works if
GSGlyph.storeProductionNameis set (see below).- Type:
str
- storeProductionName¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.productionNameof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
- tags¶
store strings that can be used to filter glyphs or build OT-classes with token filters
- Type:
list
- glyphInfo¶
GSGlyphInfoobject for this glyph with detailed information.- Type:
- sortName¶
Alternative name of glyph used for sorting in UI.
- Type:
str
- sortNameKeep¶
Alternative name of glyph used for sorting in UI, when using ‘Keep Alternates Next to Base Glyph’ from Font Info. see
GSGlyph.storeSortName:type: str
- storeSortName¶
Set to True in order to manipulate the
GSGlyph.sortNameandGSGlyph.sortNameKeepof the glyph (see above). Makes it possible to ship custom glyph data inside a .glyphs file without a separate GlyphData file. Same as Cmd-Alt-i dialog in UI.- Type:
bool
- leftKerningGroup¶
The leftKerningGroup of the glyph. All glyphs with the same text in the kerning group end up in the same kerning class.
- Type:
str
- rightKerningGroup¶
The rightKerningGroup of the glyph. All glyphs with the same text in the kerning group end up in the same kerning class.
- Type:
str
- topKerningGroup¶
The topKerningGroup of the glyph. All glyphs with the same text in the kerning group end up in the same kerning class.
- Type:
str
- bottomKerningGroup¶
The bottomKerningGroup of the glyph. All glyphs with the same text in the kerning group end up in the same kerning class.
- Type:
str
- leftKerningKey¶
The key to be used with the kerning functions (
GSFont.kerningForPair(),GSFont.setKerningForPair(),GSFont.removeKerningForPair()).If the glyph has a
leftKerningGroupattribute, the internally used @MMK_R_xx notation will be returned (note that the R in there stands for the right side of the kerning pair for LTR fonts, which corresponds to the left kerning group of the glyph). If no group is given, the glyph’s name will be returned.- Type:
str
# Set kerning for 'T' and all members of kerning class 'a' # For LTR fonts, always use the .rightKerningKey for the first (left) glyph of the pair, .leftKerningKey for the second (right) glyph. font.setKerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, font.glyphs['T'].rightKerningKey, font.glyphs['a'].leftKerningKey, -60) # which corresponds to: font.setKerningForPair(font.selectedFontMaster.id, 'T', '@MMK_R_a', -60)
- rightKerningKey¶
The key to be used with the kerning functions (
GSFont.kerningForPair(),GSFont.setKerningForPair()GSFont.removeKerningForPair()).If the glyph has a
rightKerningGroupattribute, the internally used @MMK_L_xx notation will be returned (note that the L in there stands for the left side of the kerning pair for LTR fonts, which corresponds to the right kerning group of the glyph). If no group is given, the glyph’s name will be returned.See above for an example.
- Type:
str
Added in version 2.4.
- topKerningKey¶
The key to be used with the kerning functions (
GSFont.kerningForPair(),GSFont.setKerningForPair(),GSFont.removeKerningForPair()).Added in version 3.
- bottomKerningKey¶
The key to be used with the kerning functions (
GSFont.kerningForPair(),GSFont.setKerningForPair(),GSFont.removeKerningForPair()).Added in version 3.
- leftMetricsKey¶
The leftMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- rightMetricsKey¶
The rightMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- widthMetricsKey¶
The widthMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- topMetricsKey¶
The topMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.4.
- bottomMetricsKey¶
The bottomMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.4.
- export¶
Defines whether glyph will export upon font generation
- Type:
bool
- color¶
Color marking of glyph in UI
- Type:
int
glyph.color = 0 # red glyph.color = 1 # orange glyph.color = 2 # brown glyph.color = 3 # yellow glyph.color = 4 # light green glyph.color = 5 # dark green glyph.color = 6 # light blue glyph.color = 7 # dark blue glyph.color = 8 # purple glyph.color = 9 # magenta glyph.color = 10 # light gray glyph.color = 11 # charcoal glyph.color = None # not colored, white (before version 1235, use -1)
- colorObject¶
NSColor object of glyph color, useful for drawing in plugins.
- Type:
NSColor
# use glyph color to draw the outline glyph.colorObject.set() # Get RGB (and alpha) values (as float numbers 0..1, multiply with 256 if necessary) R, G, B, A = glyph.colorObject.colorUsingColorSpace_(NSColorSpace.genericRGBColorSpace()).getRed_green_blue_alpha_(None, None, None, None) print(R, G, B) >> 0.617805719376 0.958198726177 0.309286683798 print(round(R * 256), int(G * 256), int(B * 256)) >> 158 245 245 # Draw layer glyph.layers[0].bezierPath.fill() # set the glyph color. glyph.colorObject = NSColor.colorWithDeviceRed_green_blue_alpha_(247.0 / 255.0, 74.0 / 255.0, 62.9 / 255.0, 1) # or: glyph.colorObject = (247.0, 74.0, 62.9) # max 255.0 # or: glyph.colorObject = (247.0, 74.0, 62.9, 1) # with alpha # or: glyph.colorObject = (0.968, 0.29, 0.247, 1) # max 1.0
- note¶
- Type:
str
- selected¶
Return True if the Glyph is selected in the Font View. This is different to the property font.selectedLayers which returns the selection from the active tab.
- Type:
bool
# access all selected glyphs in the Font View for glyph in font.glyphs: if glyph.selected: print(glyph)
- mastersCompatible¶
Return True when all layers in this glyph are compatible (same components, anchors, paths etc.)
- Type:
bool
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value glyph.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del glyph.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- smartComponentAxes¶
A list of
GSSmartComponentAxisobjects.These are the axis definitions for the interpolations that take place within the Smart Components. Corresponds to the ‘Properties’ tab of the glyph’s ‘Show Smart Glyph Settings’ dialog.
Also see https://glyphsapp.com/tutorials/smart-components for reference.
- Type:
list
# Adding two interpolation axes to the glyph axis1 = GSSmartComponentAxis() axis1.name = 'crotchDepth' axis1.topValue = 0 axis1.bottomValue = -100 g.smartComponentAxes.append(axis1) axis2 = GSSmartComponentAxis() axis2.name = 'shoulderWidth' axis2.topValue = 100 axis2.bottomValue = 0 g.smartComponentAxes.append(axis2) # Deleting one axis del g.smartComponentAxes[1]
- lastChange¶
Change date when glyph was last changed as datetime.
Check Python’s
timemodule for how to use the timestamp.
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the glyph
- beginUndo()¶
Call this before you do a longer running change to the glyph. Be extra careful to call
glyph.endUndo()when you are finished.
- endUndo()¶
This closes a undo group that was opened by a previous call of
glyph.beginUndo()Make sure that you call this for each beginUndo() call.
- updateGlyphInfo(changeName=True)¶
Updates all information like name, unicode etc. for this glyph.
- duplicate([name])¶
Duplicate the glyph under a new name and return it.
If no name is given, .00n will be appended to it.
GSLayer¶
Implementation of the layer object.
For details on how to access these layers, please see GSGlyph.layers
- class GSLayer¶
Properties
Functions
Properties
- name¶
Name of layer
- Type:
str
- master¶
Master that this layer is connected to. Read only.
- Type:
- associatedMasterId¶
The ID of the
fontMasterthis layer belongs to, in case this isn’t a master layer. Every layer that isn’t a master layer needs to be attached to one master layer.# add a new layer newLayer = GSLayer() newLayer.name = '{125, 100}' # (example for glyph-level intermediate master) # you may set the master ID that this layer will be associated with, otherwise the first master will be used newLayer.associatedMasterId = font.masters[-1].id # attach to last master font.glyphs['a'].layers.append(newLayer)
- Type:
str
- layerId¶
The unique layer ID is used to access the layer in the
glyphslayer dictionary.For master layers this should be the id of the
fontMaster. It could look like this:FBCA074D-FCF3-427E-A700-7E318A949AE5- Type:
str
# see ID of active layer id = font.selectedLayers[0].layerId print(id) >> FBCA074D-FCF3-427E-A700-7E318A949AE5 # access a layer by this ID layer = font.glyphs["a"].layers[id] layer = font.glyphs["a"].layers['FBCA074D-FCF3-427E-A700-7E318A949AE5'] # for master layers, use ID of masters layer = font.glyphs["a"].layers[font.masters[0].id]
- attributes¶
layer attributes like
axisRules,coordinates,colorPalette,sbixSize,color,svgaxis = font.axes[0] layer.attributes["axisRules"] = {axis.axisId: {'min': 100}} layer.attributes["coordinates"] = {axis.axisId: 99} layer.attributes["colorPalette"] = 2 # This makes the layer a CPAL layer for color index 2
- Type:
dict
- color¶
Color marking of glyph in UI
- Type:
int
glyph.color = 0 # red glyph.color = 1 # orange glyph.color = 2 # brown glyph.color = 3 # yellow glyph.color = 4 # light green glyph.color = 5 # dark green glyph.color = 6 # light blue glyph.color = 7 # dark blue glyph.color = 8 # purple glyph.color = 9 # magenta glyph.color = 10 # light gray glyph.color = 11 # charcoal glyph.color = None # not colored, white (before version 1235, use -1)
- colorObject¶
NSColor object of layer color, useful for drawing in plugins.
- Type:
NSColor
# use layer color to draw the outline layer.colorObject.set() # Get RGB (and alpha) values (as float numbers 0..1, multiply with 256 if necessary) R, G, B, A = layer.colorObject.colorUsingColorSpace_(NSColorSpace.genericRGBColorSpace()).getRed_green_blue_alpha_(None, None, None, None) print(R, G, B) >> 0.617805719376 0.958198726177 0.309286683798 print(round(R * 256), int(G * 256), int(B * 256)) >> 158 245 245 # Draw layer layer.bezierPath.fill() # set the layer color. layer.colorObject = NSColor.colorWithDeviceRed_green_blue_alpha_(247.0 / 255.0, 74.0 / 255.0, 62.9 / 255.0, 1)
- components¶
Collection of
GSComponentobjects. This is only a helper proxy to iterate all components (without paths). To add/remove items, useGSLayer.shapes.- Type:
list
for component in layer.components: print(component)
- guides¶
List of
GSGuideobjects.- Type:
list
# access all guides for guide in layer.guides: print(guide) # add guide newGuide = GSGuide() newGuide.position = NSPoint(100, 100) newGuide.angle = -10.0 layer.guides.append(newGuide) # delete guide del layer.guides[0] # copy guides from another layer import copy layer.guides = copy.copy(anotherlayer.guides)
- annotations¶
List of
GSAnnotationobjects.- Type:
list
# access all annotations for annotation in layer.annotations: print(annotation) # add new annotation newAnnotation = GSAnnotation() newAnnotation.type = TEXT newAnnotation.text = 'Fuck, this curve is ugly!' layer.annotations.append(newAnnotation) # delete annotation del layer.annotations[0] # copy annotations from another layer import copy layer.annotations = copy.copy(anotherlayer.annotations)
- hints¶
List of
GSHintobjects.- Type:
list
# access all hints for hint in layer.hints: print(hint) # add a new hint newHint = GSHint() # change behaviour of hint here, like its attachment nodes layer.hints.append(newHint) # delete hint del layer.hints[0] # copy hints from another layer import copy layer.hints = copy.copy(anotherlayer.hints) # remember to reconnect the hints’ nodes with the new layer’s nodes
- anchors¶
List of
GSAnchorobjects.- Type:
list, dict
# access all anchors: for a in layer.anchors: print(a) # add a new anchor layer.anchors['top'] = GSAnchor() # delete anchor del layer.anchors['top'] # copy anchors from another layer import copy layer.anchors = copy.copy(anotherlayer.anchors)
- shapes¶
List of
GSShapeobjects. That are most likelyGSPathorGSComponent- Type:
list
# access all shapes for shape in layer.shapes: print(shape) # delete shape del layer.shapes[0] # copy shapes from another layer import copy layer.shapes = copy.copy(anotherlayer.shapes)
- paths¶
List of
GSPathobjects. This is only a helper proxy to iterate all paths (without components). To add/remove items, useGSLayer.shapes.- Type:
list
# access all paths for path in layer.paths: print(path)
- selection¶
List of all selected objects in the glyph.
This list contains all selected items, including nodes, anchors, guides etc. If you want to work specifically with nodes, for instance, you may want to cycle through the nodes (or anchors etc.) and check whether they are selected. See example below.
- Type:
list
# access all selected nodes for path in layer.paths: for node in path.nodes: # (or path.anchors etc.) print(node.selected) # clear selection layer.clearSelection()
- LSB¶
Left sidebearing
- Type:
float
- RSB¶
Right sidebearing
- Type:
float
- TSB¶
Top sidebearing
- Type:
float
- BSB¶
Bottom sidebearing
- Type:
float
- width¶
Layer width
- Type:
float
- vertWidth¶
Layer vertical width
set it to None to reset it to default
- Type:
float
Added in version 2.6.2.
- vertOrigin¶
Layer vertical origin
set it to None to reset it to default
- Type:
float
Added in version 2.6.2.
- ascender¶
The ascender for this layer.
- Type:
float
Added in version 3.0.2.
- descender¶
The descender for this layer.
- Type:
float
Added in version 3.0.2.
- leftMetricsKey¶
The leftMetricsKey of the layer. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- rightMetricsKey¶
The rightMetricsKey of the layer. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- widthMetricsKey¶
The widthMetricsKey of the layer. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
- topMetricsKey¶
The topMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.4.
- bottomMetricsKey¶
The bottomMetricsKey of the glyph. This is a reference to another glyph by name or formula. It is used to synchronize the metrics with the linked glyph.
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.4.
- bounds¶
Bounding box of whole glyph as NSRect. Read-only.
- Type:
NSRect
# origin print(layer.bounds.origin.x, layer.bounds.origin.y) # size print(layer.bounds.size.width, layer.bounds.size.height)
- selectionBounds¶
Bounding box of the layer’s selection (nodes, anchors, components etc). Read-only.
- Type:
NSRect
- metrics¶
The metrics layer are a list of horizontal metrics filtered specifically for this layer. Use this instead of
master.alignmentZones.- Type:
Added in version 3.0.1.
- background¶
The background layer
- Type:
# copy layer to its background layer.background = layer.copy() # remove background layer layer.background = None
- backgroundImage¶
The background image. It will be scaled so that 1 em unit equals 1 of the image’s pixels.
- Type:
# set background image layer.backgroundImage = GSBackgroundImage('/path/to/file.jpg') # remove background image layer.backgroundImage = None
- bezierPath¶
The layer as an NSBezierPath object. Useful for drawing glyphs in plug-ins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.bezierPath.fill()
- openBezierPath¶
All open paths of the layer as an NSBezierPath object. Useful for drawing glyphs as outlines in plug-ins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.openBezierPath.stroke()
- completeBezierPath¶
The layer as an NSBezierPath object including paths from components. Useful for drawing glyphs in plug-ins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.completeBezierPath.fill()
- completeOpenBezierPath¶
All open paths of the layer as an NSBezierPath object including paths from components. Useful for drawing glyphs as outlines in plugins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.completeOpenBezierPath.stroke()
- isAligned¶
Indicates if the components are auto aligned.
- Type:
bool
- isSpecialLayer¶
If the layer is a brace, bracket or a smart component layer
- Type:
bool
- isMasterLayer¶
If it is a master layer
- Type:
bool
- italicAngle¶
The italic angle that applies to this layer
- Type:
float
- visible¶
if the layer is visible (the eye icon in the layer panel)
- Type:
bool
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value layer.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del layer.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use layer.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- smartComponentPoleMapping¶
Maps this layer to the poles on the interpolation axes of the Smart Glyph. The dictionary keys are the names of the
GSSmartComponentAxisobjects. The values are 1 for bottom pole and 2 for top pole. Corresponds to the ‘Layers’ tab of the glyph’s ‘Show Smart Glyph Settings’ dialog.Also see https://glyphsapp.com/tutorials/smart-components for reference.
- Type:
dict, int
# Map layers to top and bottom poles: crotchDepthAxis = glyph.smartComponentAxes['crotchDepth'] shoulderWidthAxis = glyph.smartComponentAxes['shoulderWidth'] for layer in glyph.layers: # Regular layer if layer.name == 'Regular': layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[crotchDepthAxis.id] = 2 layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[shoulderWidthAxis.id] = 2 # NarrowShoulder layer elif layer.name == 'NarrowShoulder': layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[crotchDepthAxis.id] = 2 layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[shoulderWidthAxis.id] = 1 # LowCrotch layer elif layer.name == 'LowCrotch': layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[crotchDepthAxis.id] = 1 layer.smartComponentPoleMapping[shoulderWidthAxis.id] = 2
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the layer
- decomposeComponents()¶
Decomposes all components of the layer at once.
- decomposeCorners()¶
Decomposes all corners of the layer at once.
Added in version 2.4.
- compareString()¶
Returns a string representing the outline structure of the glyph, for compatibility comparison.
- Returns:
The comparison string
- Return type:
str
print(layer.compareString()) >> oocoocoocoocooc_oocoocoocloocoocoocoocoocoocoocoocooc_
- connectAllOpenPaths()¶
Closes all open paths when end points are further than 1 unit away from each other.
- copyDecomposedLayer()¶
Returns a copy of the layer with all components decomposed.
- Returns:
A new layer object
- Return type:
- syncMetrics()¶
Take over LSB and RSB from linked glyph.
# sync metrics of all layers of this glyph for layer in glyph.layers: layer.syncMetrics()
- correctPathDirection()¶
Corrects the path direction.
- removeOverlap([checkSelection=False])¶
Joins all contours.
- Parameters:
checkSelection – If the selection will be considered. Default: False
- roundCoordinates()¶
Round the positions of all coordinates to the grid (size of which is set in the Font Info).
- addNodesAtExtremes([force=False, checkSelection=False])¶
Add nodes at layer’s extrema, e.g., top, bottom etc.
- Parameters:
force – if points are always added, even if that would distort the shape
checkSelection – only process selected segments
- applyTransform(transform)¶
Apply a transformation matrix to the layer.
layer.applyTransform([ 0.5, # x scale factor 0.0, # x skew factor 0.0, # y skew factor 0.5, # y scale factor 0.0, # x position 0.0 # y position ]) from Foundation import NSAffineTransform, NSMidX, NSMidY bounds = Layer.bounds transform = NSAffineTransform.new() transform.translateXBy_yBy_(NSMidX(bounds), NSMidY(bounds)) transform.rotateByDegrees_(-30) transform.translateXBy_yBy_(-NSMidX(bounds), -NSMidY(bounds)) Layer.applyTransform(transform)
- Parameters:
transform – a list of 6 numbers, a NSAffineTransform or a NSAffineTransformStruct
- transform(transform[, selection=False, components=True])¶
Apply a
NSAffineTransformto the layer.- Parameters:
transform – A
NSAffineTransformselection – check selection
components – if components should be transformed
transformation = NSAffineTransform() transformation.rotate(45, (200, 200)) layer.transform(transformation)
- beginChanges()¶
Call this before you do bigger changes to the Layer. This will increase performance and prevent undo problems. Always call layer.endChanges() if you are finished.
- endChanges()¶
Call this if you have called layer.beginChanges before. Make sure to group bot calls properly.
- cutBetweenPoints(Point1, Point2)¶
Cuts all paths that intersect the line from Point1 to Point2
- Parameters:
Point1 – one point
Point2 – the other point
# cut glyph in half horizontally at y=100 layer.cutBetweenPoints(NSPoint(0, 100), NSPoint(layer.width, 100))
- intersections()¶
returns a list of all intersections between overlapping paths in the layer.
- intersectionsBetweenPoints(Point1, Point2, components=False)¶
Return all intersection points between a measurement line and the paths in the layer. This is basically identical to the measurement tool in the UI.
Normally, the first returned point is the starting point, the last returned point is the end point. Thus, the second point is the first intersection, the second last point is the last intersection.
- Parameters:
Point1 – one point
Point2 – the other point
components – if components should be measured. Default: False
ignoreLocked – ignore locked or unfocused paths. Default: False
# show all intersections with glyph at y=100 intersections = layer.intersectionsBetweenPoints((-1000, 100), (layer.width+1000, 100)) print(intersections) # left sidebearing at measurement line print(intersections[1].x) # right sidebearing at measurement line print(layer.width - intersections[-2].x)
- addMissingAnchors()¶
Adds missing anchors defined in the glyph database.
- clearSelection()¶
Unselect all selected items in this layer.
- clear()¶
Remove all elements from layer.
- swapForegroundWithBackground()¶
Swap Foreground layer with Background layer.
- reinterpolate()¶
Re-interpolate a layer according the other layers and its interpolation values.
Applies to both master layers as well as brace layers and is equivalent to the ‘Re-Interpolate’ command from the Layers palette.
GSAnchor¶
Implementation of the anchor object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.anchors
- class GSAnchor([name, pt, position])¶
- Parameters:
name – the name of the anchor
pt – the position of the anchor
Properties
Functions
Properties
- position¶
The position of the anchor
- Type:
NSPoint
# read position print(layer.anchors['top'].position.x, layer.anchors['top'].position.y) # set position layer.anchors['top'].position = NSPoint(175, 575) # increase vertical position by 50 units layer.anchors['top'].position = NSPoint(layer.anchors['top'].position.x, layer.anchors['top'].position.y + 50)
- name¶
The name of the anchor
- Type:
str
- selected¶
Selection state of anchor in UI.
# select anchor layer.anchors[0].selected = True # log selection state print(layer.anchors[0].selected)
- Type:
bool
- orientation¶
If the position of the anchor is relative to the LSB (0), center (2) or RSB (1).
- Type:
int
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value anchor.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del component.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
Added in version 3.
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the anchor
- attributes¶
attributes attributes like
identifiercomponent.attributes['identifier'] = "220238F0"
- Type:
dict
GSComponent¶
Implementation of the component object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.components
- class GSComponent(glyph[, position])¶
- Parameters:
glyph – a
GSGlyphobject or the glyph nameposition – the position of the component as NSPoint
Properties
Functions
Properties
- position¶
The position of the component.
- Type:
NSPoint
- scale¶
Scale factor of the component.
A tuple containing the horizontal and vertical scale.
- Type:
tuple, NSPoint
- rotation¶
Rotation angle of the component.
- Type:
float
- slant¶
The slant of the component.
- Type:
tuple, NSPoint
- componentName¶
The glyph name the component is pointing to.
- Type:
str
- name¶
The glyph name the component is pointing to.
- Type:
str
Added in version 2.5.
- componentMasterId¶
The ID of the master to component is pointing to.
- Type:
str
Added in version 3.1.
- component¶
The
GSGlyphthe component is pointing to. This is read-only. In order to change the referenced base glyph, setcomponentNameto the new glyph name.- Type:
- componentLayer¶
The
GSLayerthe component is pointing to. This is read-only. In order to change the referenced base glyph, setcomponentNameto the new glyph name.For Smart Components, the componentLayer contains the interpolated result.
- Type:
Added in version 2.5.
- transform¶
Transformation matrix of the component. If Glyphs 3, this is computed from the scale, rotation and position.
- Type:
NSAffineTransformStruct
component.transform = (( 0.5, # x scale factor 0.0, # x skew factor 0.0, # y skew factor 0.5, # y scale factor 0.0, # x position 0.0 # y position ))
- bounds¶
Bounding box of the component, read-only
- Type:
NSRect
component = layer.components[0] # first component # origin print(component.bounds.origin.x, component.bounds.origin.y) # size print(component.bounds.size.width, component.bounds.size.height)
- automaticAlignment¶
Defines whether the component is automatically aligned.
- Type:
bool
- alignment¶
See Component Alignment for available constants.
Added in version 2.5.
- locked¶
Added in version 2.5.
If the component is locked TODO
- Type:
bool
- anchor¶
If more than one anchor/_anchor pair would match, this property can be used to set the anchor to use for automatic alignment
This can be set from the anchor button in the component info box in the UI
- Type:
str
- selected¶
Selection state of component in UI.
- Type:
bool
# select component layer.components[0].selected = True # print(selection state) print(layer.components[0].selected)
- attributes¶
attributes attributes like
maskorreversePathscomponent.attributes['mask'] = True component.attributes['reversePaths'] = True
- Type:
dict
- smartComponentValues¶
Dictionary of interpolations values of the Smart Component. Key are the axis.id, values are between the top and the bottom value of the corresponding
GSSmartComponentAxisobjects. Corresponds to the values of the ‘Smart Component Settings’ dialog. Returns None if the component is not a Smart Component.For newly setup smart glyphs, the axis.id is a random string. After saving and re-opening the file, the name and id is the same. As long as you don’t change the name. So it is saver to always go through the smart glyphs > axis > id (as explained in the code sample below.
Also see https://glyphsapp.com/tutorials/smart-components for reference.
- Type:
dict, int
component = glyph.layers[0].shapes[1] widthAxis = component.component.smartComponentAxes['Width'] # get the width axis from the smart glyph components.smartComponentValues[widthAxis.id] = 45 # Check whether a component is a smart component for component in layer.components: if component.smartComponentValues is not None: # do stuff
- bezierPath¶
The component as an NSBezierPath object. Useful for drawing glyphs in plugins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.components[0].bezierPath.fill()
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value component.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del component.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
Added in version 2.5.
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use component.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value component.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del component.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
Functions
- applyTransform()¶
Apply a transformation matrix to the component.
component = layer.components[0] component.applyTransform(( 0.5, # x scale factor 0.0, # x skew factor 0.0, # y skew factor 0.5, # y scale factor 0.0, # x position 0.0 # y position ))
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the component
- decompose([doAnchors=True, doHints=True])¶
Decomposes the component.
- Parameters:
doAnchors – get anchors from components
doHints – get hints from components
GSGlyphReference¶
a small helper class to store a reference to a glyph in userData that will keep track of changes to the glyph name.
Added in version 3.0.4.
GSSmartComponentAxis¶
Implementation of the Smart Component interpolation axis object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSGlyph.smartComponentAxes
Added in version 2.3.
- class GSSmartComponentAxis¶
Properties
Properties
- name¶
Name of the axis. The name is for display purpose only.
- Type:
str
- id¶
Id of the axis. This Id will be used to map the Smart Glyph’s layers to the poles of the interpolation. See
GSLayer.smartComponentPoleMapping- Type:
str
Added in version 2.5.
- topValue¶
Top end (pole) value on interpolation axis.
- Type:
int, float
- bottomValue¶
Bottom end (pole) value on interpolation axis.
- Type:
int, float
GSShape¶
Implementation of the shape object. This a superclass for GSPath and GSComponent. You can’t instantiate GSShape directly
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.shapes
GSPath¶
Implementation of the path object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.paths
If you build a path in code, make sure that the structure is valid. A curve node has to be preceded by two off-curve nodes. And an open path has to start with a line node.
- class GSPath¶
Properties
Functions
Properties
- nodes¶
A list of
GSNodeobjects- Type:
list
# access all nodes for path in layer.paths: for node in path.nodes: print(node)
- segments¶
A list of segments as NSPoint objects. Two objects represent a line, four represent a curve. Start point of the segment is included.
- Type:
list
# access all segments for path in layer.paths: for segment in path.segments: print(segment)
- closed¶
Returns True if the the path is closed
- Type:
bool
- direction¶
Path direction. -1 for counter clockwise, 1 for clockwise.
- Type:
int
- bounds¶
Bounding box of the path, read-only
- Type:
NSRect
path = layer.paths[0] # first path # origin print(path.bounds.origin.x, path.bounds.origin.y) # size print(path.bounds.size.width, path.bounds.size.height)
- selected¶
Selection state of path in UI.
- Type:
bool
# select path layer.paths[0].selected = True # print(selection state) print(layer.paths[0].selected)
- bezierPath¶
The same path as an NSBezierPath object. Useful for drawing glyphs in plugins.
- Type:
NSBezierPath
# draw the path into the Edit view NSColor.redColor().set() layer.paths[0].bezierPath.fill()
Functions
- reverse()¶
Reverses the path direction
- attributes¶
path attributes like
fill,mask,strokeWidth,strokeHeight,strokeColor',strokePos# in B/W layers: path.attributes['fill'] = True path.attributes['mask'] = True path.attributes['strokeWidth'] = 100 path.attributes['strokeHeight'] = 80 # in color layers: path.attributes['strokeColor'] = NSColor.redColor() path.attributes['fillColor'] = NSColor.blueColor() path.attributes['strokePos'] = 1 # or 0, -1
- Type:
dict
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use path.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value path.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del path.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
draw the object with a fontTools pen
- addNodesAtExtremes([force=False, checkSelection=False])¶
Add nodes at path’s extrema, e.g., top, bottom etc.
- Parameters:
force – if points are always added, even if that would distort the shape
checkSelection – only process selected segments
- applyTransform()¶
Apply a transformation matrix to the path.
path = layer.paths[0] path.applyTransform(( 0.5, # x scale factor 0.0, # x skew factor 0.0, # y skew factor 0.5, # y scale factor 0.0, # x position 0.0 # y position ))
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the path
GSNode¶
Implementation of the node object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSPath.nodes
- class GSNode([pt, type=type])¶
- Parameters:
pt – The position of the node.
type – The type of the node, LINE, CURVE or OFFCURVE
Properties
Functions
Properties
- position¶
The position of the node.
- Type:
NSPoint
- type¶
The type of the node, LINE, CURVE or OFFCURVE
Always compare against the constants, never against the actual value.
- Type:
str
- smooth¶
If it is a smooth connection or not
- Type:
BOOL
- connection¶
The type of the connection, SHARP or SMOOTH
- Type:
str
Deprecated since version 2.3: Use
smoothinstead.
- selected¶
Selection state of node in UI.
- Type:
bool
# select node layer.paths[0].nodes[0].selected = True # print(selection state) print(layer.paths[0].nodes[0].selected)
- index¶
Returns the index of the node in the containing path or maxint if it is not in a path.
- Type:
int
- nextNode¶
Returns the next node in the path.
Please note that this is regardless of the position of the node in the path and will jump across the path border to the beginning of the path if the current node is the last.
If you need to take into consideration the position of the node in the path, use the node’s index attribute and check it against the path length.
- Type:
print(layer.paths[0].nodes[0].nextNode # returns the second node in the path (index 0 + 1)) print(layer.paths[0].nodes[-1].nextNode # returns the first node in the path (last node >> jumps to beginning of path)) # check if node is last node in path (with at least two nodes) print(layer.paths[0].nodes[0].index == (len(layer.paths[0].nodes) - 1)) # returns False for first node print(layer.paths[0].nodes[-1].index == (len(layer.paths[0].nodes) - 1)) # returns True for last node
- prevNode¶
Returns the previous node in the path.
Please note that this is regardless of the position of the node in the path, and will jump across the path border to the end of the path if the current node is the first.
If you need to take into consideration the position of the node in the path, use the node’s index attribute and check it against the path length.
- Type:
print(layer.paths[0].nodes[0].prevNode) # returns the last node in the path (first node >> jumps to end of path) print(layer.paths[0].nodes[-1].prevNode) # returns second last node in the path # check if node is first node in path (with at least two nodes) print(layer.paths[0].nodes[0].index == 0) # returns True for first node print(layer.paths[0].nodes[-1].index == 0) # returns False for last node
- name¶
Attaches a name to a node.
- Type:
str
- orientation¶
If the position of the node is relative to the LSB (0), center (2) or RSB (1).
- Type:
int
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value node.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del node.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
Added in version 2.4.1.
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the node
- makeNodeFirst()¶
Turn this node into the start point of the path.
- toggleConnection()¶
Toggle between sharp and smooth connections.
GSPathSegment¶
Implementation of the segment object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSPath.segments
- class GSPathSegment¶
Properties
Functions
- bounds¶
Bounding box of the segment as NSRect. Read-only.
- Type:
NSRect
bounds = segment.bounds # origin print(bounds.origin.x, bounds.origin.y) # size print(bounds.size.width, bounds.size.height)
- type¶
The type of the node, LINE, CURVE or QCURVE
Always compare against the constants, never against the actual value.
- Type:
str
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the segment
- reverse()¶
reverses the segments
- middlePoint()¶
the point at t=0.5
- lastPoint()¶
the ending point of the segment
- inflectionPoints()¶
a list of “t” values of inflection points on the segment
- curvatureAtTime_(t)¶
the curvature at “t”
- pointAtTime_(t)¶
the point a “t”
- normalAtTime_(t)¶
the normal vector at “t”
- tangentAtTime_(t)¶
the tangent at “t”
- extremePoints()¶
a list of extreme points
- extremeTimes()¶
a list of “t” value for the extreme points
- normalizeHandles()¶
balances the length of the handle while trying to keep the shape as good as possible
GSGuide¶
Implementation of the guide object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.guides
- class GSGuide¶
Properties
Functions
- lockAngle¶
locks the angle
- Type:
bool
- angle¶
Angle
- Type:
float
- name¶
a optional name
- Type:
str
- selected¶
Selection state of guide in UI.
- Type:
bool
# select guide layer.guides[0].selected = True # print(selection state) print(layer.guides[0].selected)
- locked¶
Locked
- Type:
bool
- filter¶
A filter to only show the guide in certain glyphs. Only relevant in global guides
- Type:
NSPredicate
- showMeasurement¶
If the guide is showing measurements
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.1.
- userData¶
A dictionary to store user data. Use a unique key and only use objects that can be stored in a property list (string, list, dict, numbers, NSData) otherwise the data will not be recoverable from the saved file.
- Type:
dict
# set value guide.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del guide.userData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
Functions
- copy()¶
Returns a full copy of the guide
GSAnnotation¶
Implementation of the annotation object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.annotations
GSHint¶
Implementation of the hint object.
For details on how to access them, please see GSLayer.hints
- class GSHint¶
Properties
- originNode¶
The first node the hint is attached to.
- Type:
GSNodeorGSHandle(e.g. when attached to intersections)
- targetNode¶
The the second node this hint is attached to. In the case of a ghost hint, this value will be empty.
- Type:
GSNodeorGSHandle(e.g. when attached to intersections)
- otherNode1¶
A third node this hint is attached to. Used for Interpolation or Diagonal hints.
- Type:
GSNodeorGSHandle(e.g. when attached to intersections)
- otherNode2¶
A fourth node this hint is attached to. Used for Diagonal hints.
- Type:
GSNodeorGSHandle(e.g. when attached to intersections)
- originIndex¶
The indexPath to the first node the hint is attached to.
- Type:
NSIndexPath
- targetIndex¶
The indexPath to the second node this hint is attached to. In the case of a ghost hint, this value will be empty.
- Type:
NSIndexPath
- otherIndex1¶
A indexPath to the third node this hint is attached to. Used for Interpolation or Diagonal hints.
- Type:
NSIndexPath
- otherIndex2¶
A indexPath to the fourth node this hint is attached to. Used for Diagonal hints.
- Type:
NSIndexPath
- type¶
See Hint Types
- Type:
int
- options¶
Stores extra options for the hint. For TT hints, that might be the rounding settings.
See Hint Option
For corner components, it stores the alignment settings: left = 0, center = 2, right = 1, auto (for caps) = alignment | 8
- Type:
int
- horizontal¶
True if hint is horizontal, False if vertical.
- Type:
bool
- selected¶
Selection state of hint in UI.
- Type:
bool
# select hint layer.hints[0].selected = True # print(selection state) print(layer.hints[0].selected)
- name¶
Name of the hint. This is the referenced glyph for corner and cap components.
- Type:
str
- stem¶
Index of TrueType stem that this hint is attached to. The stems are defined in the custom parameter “TTFStems” per master.
For no stem, value is -1.
For automatic, value is -2.
- Type:
int
- isTrueType¶
if it is a TrueType instruction
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.
- isPostScript¶
if it is a PostScript hint
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.
- isCorner¶
if it is a Corner (or Cap, Brush…) component
- Type:
bool
Added in version 3.
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. (If you need the data persistent, use hint.settings() (not documented, yet))
- Type:
dict
# set value hint.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del hint.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
GSBackgroundImage¶
Implementation of background image.
For details on how to access it, please see GSLayer.backgroundImage
- class GSBackgroundImage([path])¶
- Parameters:
path – Initialize with an image file (optional)
Properties
Functions
Properties
- path¶
Path to image file.
- Type:
str
- image¶
NSImageobject of background image, read-only (as in: not settable)- Type:
NSImage
- crop¶
Crop rectangle. This is relative to the image size in pixels, not the font’s em units (just in case the image is scaled to something other than 100%).
- Type:
NSRect
# change cropping layer.backgroundImage.crop = NSRect(NSPoint(0, 0), NSPoint(1200, 1200))
- locked¶
Defines whether image is locked for access in UI.
- Type:
bool
- alpha¶
Defines the transparence of the image in the Edit view. Default is 50%, possible values are 10–100.
To reset it to default, set it to anything other than the allowed values.
- Type:
int
- position¶
Position of image in font units.
- Type:
NSPoint
# change position layer.backgroundImage.position = NSPoint(50, 50)
- scale¶
Scale factor of image.
A scale factor of 1.0 (100%) means that 1 font unit is equal to 1 point.
Set the scale factor for x and y scale simultaneously with an integer or a float value. For separate scale factors, please use a tuple.
- Type:
tuple, NSPoint
# change scale layer.backgroundImage.scale = 1.2 # changes x and y to 120% layer.backgroundImage.scale = (1.1, 1.2) # changes x to 110% and y to 120%
- rotation¶
Rotation angle of image.
- Type:
float
- slant¶
The slant of the image.
- Type:
tuple, NSPoint
- transform¶
Transformation matrix.
- Type:
NSAffineTransformStruct
# change transformation layer.backgroundImage.transform = (( 1.0, # x scale factor 0.0, # x skew factor 0.0, # y skew factor 1.0, # y scale factor 0.0, # x position 0.0 # y position ))
Functions
- resetCrop()¶
Resets the cropping to the image’s original dimensions.
- scaleWidthToEmUnits()¶
Scale the image’s cropped width to a certain em unit value, retaining its aspect ratio.
# fit image in layer’s width layer.backgroundImage.scaleWidthToEmUnits(layer.width)
- scaleHeightToEmUnits()¶
Scale the image’s cropped height to a certain em unit value, retaining its aspect ratio.
# position image’s origin at descender line layer.backgroundImage.position = NSPoint(0, font.masters[0].descender) # scale image to UPM value layer.backgroundImage.scaleHeightToEmUnits(font.upm)
GSGradient¶
Implementation of the gradient object.
- class GSGradient¶
Properties
Properties
- colors¶
A list of colors. Each is an list containing a NSColor and and position between 0.0 and 1.0.
- Type:
list
- type¶
The gradient type. Linear = 0, Circular = 1
- Type:
int
- start¶
A NSPoint that relatively to the shapes bounding box defines the starting point of the gradient
- Type:
NSPoint
- end¶
A NSPoint that relatively to the shapes bounding box defines the ending point of the gradient
- Type:
NSPoint
- absoluteStart¶
A NSPoint of the absolute starting point of the gradient
- Type:
NSPoint
- absoluteEnd¶
A NSPoint of the absolute ending point of the gradient
- Type:
NSPoint
GSEditViewController¶
Implementation of the GSEditViewController object, which represents Edit tabs in the UI.
For details on how to access them, please look at GSFont.tabs
- class GSEditViewController¶
Properties
Functions
Properties
- text¶
The text of the tab, either as text, or slash-escaped glyph names, or mixed. OpenType features will be applied after the text has been changed.
- Type:
str
string = "" for layer in font.selectedLayers: string += "/" + layer.parent.name tab = font.tabs[-1] tab.text = string
- string¶
The plain underlying string of the tab
- Type:
str
string = "" for layer in font.selectedLayers: char = font.characterForGlyph(layer.parent) string += chr(char) tab = font.tabs[-1] tab.text = string
Added in version 3.2.
- masterIndex¶
The index of the active master (selected in the toolbar).
- Type:
int
Added in version 2.6.1.
- layers¶
Alternatively, you can set (and read) a list of
GSLayerobjects. These can be any of the layers of a glyph.- Type:
list
layers = [] # display all layers of one glyph next to each other for layer in font.glyphs['a'].layers: layers.append(layer) # append line break layers.append(GSControlLayer(10)) # 10 being the ASCII code of the new line character (\n) font.tabs[0].layers = layers
- composedLayers¶
Similar to the above, but this list contains the
GSLayerobjects after the OpenType features have been applied (seeGSEditViewController.features). Read-only.Deprecated. .layers behave like this now.
- Type:
list
Added in version 2.4.
- scale¶
Scale (zoom factor) of the Edit view. Useful for drawing activity in plugins.
The scale changes with every zoom step of the Edit view. So if you want to draw objects (e.g. text, stroke thickness etc.) into the Edit view at a constant size relative to the UI (e.g. constant text size on screen), you need to calculate the object’s size relative to the scale factor. See example below.
- Type:
float
print(font.currentTab.scale) >> 0.414628537193 # Calculate text size desiredTextSizeOnScreen = 10 #pt scaleCorrectedTextSize = desiredTextSizeOnScreen / font.currentTab.scale print(scaleCorrectedTextSize) >> 24.1179733255
- viewPort¶
The visible area of the Edit view in screen pixel coordinates (view coordinates).
The NSRect’s origin value describes the top-left corner (top-right for RTL, both at ascender height) of the combined glyphs’ bounding box (see
bounds), which also serves as the origin of the view plane.The NSRect’s size value describes the width and height of the visible area.
When using drawing methods such as the view-coordinate-relative method in the Reporter Plugin, use these coordinates.
- Type:
NSRect
# The far corners of the Edit view: # Lower left corner of the screen x = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.x y = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.y # Top left corner of the screen x = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.x y = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.y + font.currentTab.viewPort.size.height # Top right corner of the screen x = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.x + font.currentTab.viewPort.size.width y = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.y + font.currentTab.viewPort.size.height # Bottom right corner of the screen x = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.x + font.currentTab.viewPort.size.width y = font.currentTab.viewPort.origin.y
- bounds¶
Bounding box of all glyphs in the Edit view in view coordinate values.
- Type:
NSRect
- selectedLayerOrigin¶
Position of the active layer’s origin (0,0) relative to the origin of the view plane (see
bounds), in view coordinates.- Type:
NSPoint
- textCursor¶
Position of text cursor in text, starting with 0.
- Type:
integer
- textRange¶
Amount of selected glyphs in text, starting at cursor position (see above).
- Type:
integer
- layersCursor¶
Position of cursor in the layers list, starting with 0.
See also
GSEditViewController.layers
- Type:
integer
Added in version 2.4.
- direction¶
Writing direction.
- Type:
integer
font.currentTab.direction = GSRTL
- features¶
List of OpenType features applied to text in Edit view.
- Type:
list
font.currentTab.features = ['locl', 'ss01']
- tempData¶
A dictionary to store data temporarily. Use a unique key. This will not be saved to file. If you need the data persistent, use layer.userData
- Type:
dict
# set value layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee'] = True # delete value del layer.tempData['rememberToMakeCoffee']
- previewInstances¶
Instances to show in the Preview area.
Values are
'live'for the preview of the current content of the Edit view,'all'for interpolations of all instances of the current glyph, or individual GSInstance objects.- Type:
str/GSInstance
# Live preview of Edit view font.currentTab.previewInstances = 'live' # Text of Edit view shown in particular Instance interpolation (last defined instance) font.currentTab.previewInstances = font.instances[-1] # All instances of interpolation font.currentTab.previewInstances = 'all'
- previewHeight¶
Height of the preview panel in the Edit view in pixels.
Needs to be set to 16 or higher for the preview panel to be visible at all. Will return 0 for a closed preview panel or the current size when visible.
- Type:
float
- bottomToolbarHeight¶
Height of the little toolbar at the very bottom of the window. Read-only.
- Type:
float
Added in version 2.4.
Functions
- close()¶
Close this tab.
- saveToPDF(path[, rect])¶
Save the view to a PDF file.
- Parameters:
path – Path to the file
rect – Optional. NSRect defining the view port. If omitted,
GSEditViewController.viewPortwill be used.
Added in version 2.4.
- redraw()¶
forces a update of the edit view
GSGlyphInfo¶
Implementation of the GSGlyphInfo object.
This contains valuable information from the glyph database. See GSGlyphsInfo for how to create these objects.
- class GSGlyphInfo¶
Properties
Properties
- name¶
Human-readable name of glyph (“nice name”).
- Type:
str
- productionName¶
Production name of glyph. Will return a value only if production name differs from nice name, otherwise None.
- Type:
str
- category¶
This is mostly from the UnicodeData.txt file from unicode.org. Some corrections have been made (Accents, …) e.g: “Letter”, “Number”, “Punctuation”, “Mark”, “Separator”, “Symbol”, “Other”
- Type:
str
- subCategory¶
This is mostly from the UnicodeData.txt file from unicode.org. Some corrections and additions have been made. e.g: “Nonspacing”, “Ligature”, “Decimal Digit”, …
- Type:
str
- case¶
e.g: GSUppercase, GSLowercase, GSSmallcaps
- Type:
int
- components¶
This glyph may be composed of the glyphs returned as a list of
GSGlyphInfoobjects.- Type:
list
- accents¶
This glyph may be combined with these accents, returned as a list of glyph names.
- Type:
list
- anchors¶
Anchors defined for this glyph, as a list of anchor names.
- Type:
list
- unicode¶
Unicode value
- Type:
str
- unicode2¶
a second unicode value it present
- Type:
str
- script¶
Script of glyph, e.g: “latin”, “cyrillic”, “greek”.
- Type:
str
- index¶
Index of glyph in database. Used for sorting in UI.
- Type:
str
- sortName¶
Alternative name of glyph used for sorting in UI.
- Type:
str
- sortNameKeep¶
Alternative name of glyph used for sorting in UI, when using ‘Keep Alternates Next to Base Glyph’ from Font Info.
- Type:
str
- desc¶
Unicode description of glyph.
- Type:
str
- altNames¶
Alternative names for glyphs that are not used, but should be recognized (e.g., for conversion to nice names).
- Type:
str
- direction¶
Writing direction.
- Type:
integer
glyph.direction = GSRTL
Added in version 3.
GSFontInfoValueLocalized¶
The GSFontInfoValueLocalized
- class GSFontInfoValueLocalized¶
Properties
Properties
- key¶
the key
- Type:
str
# searching for GSFontInfoValueLocalized with given "designers" key for fontInfo in font.properties: if fontInfo.key == "designers": print(fontInfo)
- values¶
A list of
GSFontInfoValueobjects.- Type:
list
# listing values of GSFontInfoValueLocalized for fontInfoValue in fontInfoValueLocalized.values: print(fontInfoValue)
- defaultValue¶
the value that is considered the default (either the dflt or English entry)
- Type:
str
# prints the default value for given GSFontInfoValueLocalized instance print(fontInfoValueLocalized.defaultValue) # The print below will always return True, because # font.designer represent the same value fontInfoValueLocalized = None for fontInfo in font.properties: if fontInfo.key == "designers": fontInfoValueLocalized = fontInfo print(fontInfoValueLocalized.defaultValue == font.designer)
GSFontInfoValueSingle¶
The GSFontInfoValueSingle
- class GSFontInfoValueSingle¶
Properties
Properties
- key¶
the key
- Type:
str
# GSFontInfoValueSingle is stored in e.g. font.properties # one of the differences between GSFontInfoValueSingle and GSFontInfoValueLocalized # is that the first doesn't have "values" attribute for fontProperty in font.properties: if not hasattr(fontProperty, "values"): print(fontProperty.key)
- value¶
The value
- Type:
str
# GSFontInfoValueSingle is stored in e.g. font.properties # one of the differences between GSFontInfoValueSingle and GSFontInfoValueLocalized # is that the first doesn't have "values" attribute for fontProperty in font.properties: if not hasattr(fontProperty, "values"): print(fontProperty.value)
GSFontInfoValue¶
The GSFontInfoValue
- class GSFontInfoValue¶
Properties
- key¶
the key
- Type:
str
# GSFontInfoValue is stored in e.g. values attribute of font.properties for fontProperty in font.properties: # not all of font.properties contains this attribute # so we are going to look for those, that have it if hasattr(fontProperty, "values"): for fontInfoValue in fontProperty.values: # this line prints out the key attribute of # found GSFontInfoValue instance print(fontInfoValue.key)
- value¶
The value
- Type:
str
# GSFontInfoValue is stored in e.g. values attribute of font.properties for fontProperty in font.properties: # not all of font.properties contains this attribute # so we are going to look for those, that have it if hasattr(fontProperty, "values"): for fontInfoValue in fontProperty.values: # this line prints out the value attribute of # found GSFontInfoValue instance print(fontInfoValue.value)
- languageTag¶
The languageTag
- Type:
str
# GSFontInfoValue is stored in e.g. values attribute of font.properties for fontProperty in font.properties: # not all of font.properties contains this attribute # so we are going to look for those, that have it if hasattr(fontProperty, "values"): for fontInfoValue in fontProperty.values: # this line prints out the languageTag attribute of # found GSFontInfoValue instance print(fontInfoValue.languageTag)
GSMetricValue¶
The GSMetricValue objects represent vertical metrics values and theirs overshoots.
- class GSMetricValue¶
Properties
- position¶
The y position of the metric.
- Type:
float
- overshoot¶
Value of overshoot’s width.
- Type:
float
- name¶
The name of the metric value. Eg. Descender, Small Cap, Cap Height etc.
- Type:
str
- filter¶
A filter to limit the scope of the metric.
- Type:
NSPredicate
- metric¶
Corresponding GSMetric object. see
GSFont.metrics.- Type:
PreviewTextWindow¶
The Text Preview Window
- class PreviewTextWindow¶
Properties
Functions
Properties
- text¶
The text
- Type:
str
- instanceIndex¶
The index of the selected instance
- Type:
int
- fontSize¶
The font size
- Type:
int
- open()¶
opens the Preview Text Window
# open PreviewTextWindow PreviewTextWindow.open() # setting instance in PreviewTextWindow to "Regular" font = PreviewTextWindow.font instanceNames = [instance.name for instance in font.instances] regularIndex = instanceNames.index("Regular") PreviewTextWindow.instanceIndex = regularIndex # setting text and font size value PreviewTextWindow.text = 'hamburgefontsiv' PreviewTextWindow.fontSize = 200
- reloadFont()¶
- refreshes the Preview Text Window
- close()¶
- closes the Preview Text Window
NSAffineTransform¶
The NSAffineTransform object.
- class NSAffineTransform¶
Properties
Functions
Functions
- shift(x, y)¶
shift by x, y
- Type:
tuple or NSPoint
- scale(x[, y])¶
if a single number, scale uniformly, otherwise scale by x, y if center is given, that is used as the origin of the scale
- Type:
int/float or tuple
- rotate(angle)¶
- The angle of the rotation. In degree, positive angles are CCW
- if center is given, that is used as the origin of the rotation
- Type:
int/float
- skew(x[, center])¶
- if a single number, skew in x-direction otherwise skew by x, y
- if center is given, that is used as the origin of the skew
- Type:
int/float or tuple
Properties
- matrix¶
a transform matrix (m11, m12, m21, m22, x, y)
- Type:
tuple
Methods¶
- divideCurve(P0, P1, P2, P3, t)¶
Divides the curve using the De Casteljau’s algorithm.
- Parameters:
P0 – The Start point of the Curve (NSPoint)
P1 – The first off curve point
P2 – The second off curve point
P3 – The End point of the Curve
t – The time parameter
- Returns:
A list of points that represent two curves. (Q0, Q1, Q2, Q3, R1, R2, R3). Note that the ‘middle’ point is only returned once.
- Return type:
list
- distance(P0, P1)¶
calculates the distance between two NSPoints
- Parameters:
P0 – a NSPoint
P1 – another NSPoint
- Returns:
The distance
- Return type:
float
- addPoints(P1, P2)¶
Add the points.
- Parameters:
P0 – a NSPoint
P1 – another NSPoint
- Returns:
The sum of both points
- Return type:
NSPoint
- subtractPoints(P1, P2)¶
Subtracts the points.
- Parameters:
P0 – a NSPoint
P1 – another NSPoint
- Returns:
The subtracted point
- Return type:
NSPoint
- scalePoint(P, scalar)¶
Scaled a point.
- Parameters:
P – a NSPoint
scalar – The multiplier
- Returns:
The multiplied point
- Return type:
NSPoint
- removeOverlap(paths)¶
removes the overlaps from the list of paths
paths = [path1, path2, path3] mergePaths = removeOverlap(paths)
- Parameters:
paths – A list of paths
- Returns:
The resulting list of paths
- Return type:
list
- subtractPaths(paths, subtract)¶
removes the overlaps from the list of paths
- Parameters:
paths – a list of paths
subtract – the subtracting paths
- Returns:
The resulting list of paths
- Return type:
list
- intersectPaths(paths, otherPaths)¶
removes the overlaps from the list of paths
- Parameters:
paths – a list of paths
otherPaths – the other paths
- Returns:
The resulting list of paths
- Return type:
list
- GetSaveFile(message=None, ProposedFileName=None, filetypes=None)¶
Opens a file chooser dialog.
- Parameters:
message
filetypes
ProposedFileName
- Returns:
The selected file or None
- Return type:
str
- GetOpenFile(message=None, allowsMultipleSelection=False, filetypes=None, path=None)¶
Opens a file chooser dialog.
- Parameters:
message – A message string.
allowsMultipleSelection – Boolean, True if user can select more than one file
filetypes – list of strings indicating the filetypes, e.g., [“gif”, “pdf”]
path – The initial directory path
- Returns:
The selected file or a list of file names or None
- Return type:
str or list
- GetFolder(message=None, allowsMultipleSelection=False, path=None)¶
Opens a folder chooser dialog.
- Parameters:
message
allowsMultipleSelection
path
- Returns:
The selected folder or None
- Return type:
str
- Message(message, title='Alert', OKButton=None)¶
Shows an alert panel.
- Parameters:
message – the string
title – a title of the dialog
OKButton – the label of the confirmation button
- AskString(message, value=None, title='Glyphs', OKButton=None, placeholder=None)¶
AskString Dialog
- Parameters:
message – the string
value – a default value
title – a title of the dialog
OKButton – the label of the confirmation button
placeholder – a placeholder value that is displayed in gray when the text field is empty
- Returns:
the string
- Return type:
str
- PickGlyphs(content=None, masterID=None, searchString=None, defaultsKey=None)¶
Shows a dialog to select a glyph and returns the selected glyphs.
- Parameters:
content – a list of glyphs from with to pick from (e.g. filter for corner components)
masterID – The master ID to use for the previews
searchString – to pre-populate the search
defaultsKey – The userDefaults to read and store the search key. Setting this will ignore the searchString
- Returns:
the list of selected glyphs and the typed search string
- Return type:
tuple(list, str)
Added in version 3.2.
- LogToConsole(message)¶
Write a message to the Mac’s Console.app for debugging.
- Parameters:
message (str)
- LogError(message)¶
Log an error message and write it to the Macro window’s output (in red).
- Parameters:
message
Constants¶
Node Types¶
- LINE¶
Line node.
- CURVE¶
Curve node. Make sure that each curve node is preceded by two off-curve nodes.
- QCURVE¶
Quadratic curve node. Make sure that each curve node is preceded by at least one off-curve node.
- OFFCURVE¶
Off-curve node
Path Attributes¶
- FILL¶
fill
- FILLCOLOR¶
fillColor
- FILLPATTERNANGLE¶
fillPatternAngle
- FILLPATTERNBLENDMODE¶
fillPatternBlendMode
- FILLPATTERNFILE¶
fillPatternFile
- FILLPATTERNOFFSET¶
fillPatternOffset
- FILLPATTERNSCALE¶
fillPatternScale
- STROKECOLOR¶
strokeColor
- STROKELINECAPEND¶
lineCapEnd
- STROKELINECAPSTART¶
lineCapStart
- STROKELINEJOIN¶
lineJoin
- STROKEPOSITION¶
strokePos
- STROKEWIDTH¶
strokeWidth
- STROKEHEIGHT¶
strokeHeight
- GRADIENT¶
gradient
- SHADOW¶
shadow
- INNERSHADOW¶
shadowIn
- MASK¶
mask
File Format Versions¶
A constant that is used when saving are reading .glyphs file but also for the clipboard.
- GSFormatVersion1¶
The Format used by Glyphs 2
- GSFormatVersion3¶
The Format used by Glyphs 3
- GSFormatVersionCurrent¶
This will always return the format of the current app.
Export Formats¶
- OTF¶
Write CFF based font
- TTF¶
Write CFF based font
- VARIABLE¶
Write Variable font
- UFO¶
Write UFO based font
- WOFF¶
Write WOFF
- WOFF2¶
Write WOFF
- PLAIN¶
do not package as webfont
Added in version 2.5.
Info Property Keys¶
- GSPropertyNameFamilyNamesKey¶
Family Names
- GSPropertyNameDesignersKey¶
Designers
- GSPropertyNameDesignerURLKey¶
Designer URL
- GSPropertyNameManufacturersKey¶
Manufacturers
- GSPropertyNameManufacturerURLKey¶
Manufacturer URL
- GSPropertyNameCopyrightsKey¶
Copyrights
- GSPropertyNameVersionStringKey¶
Version String
- GSPropertyNameVendorIDKey¶
VendorID
- GSPropertyNameUniqueIDKey¶
UniqueID
- GSPropertyNameLicensesKey¶
Licenses
- GSPropertyNameLicenseURLKey¶
License URL
- GSPropertyNameTrademarksKey¶
Trademarks
- GSPropertyNameDescriptionsKey¶
Descriptions
- GSPropertyNameSampleTextsKey¶
SampleTexts
- GSPropertyNamePostscriptFullNamesKey¶
PostscriptFullNames
- GSPropertyNamePostscriptFontNameKey¶
PostscriptFontName
- GSPropertyNameCompatibleFullNamesKey¶
CompatibleFullNames
- GSPropertyNameStyleNamesKey¶
StyleNames
- GSPropertyNameStyleMapFamilyNamesKey¶
StyleMapFamilyNames
- GSPropertyNameStyleMapStyleNamesKey¶
StyleMapStyleNames
- GSPropertyNamePreferredFamilyNamesKey¶
PreferredFamilyNames
- GSPropertyNamePreferredSubfamilyNamesKey¶
PreferredSubfamilyNames
- GSPropertyNameVariableStyleNamesKey¶
VariableStyleNames
- GSPropertyNameWWSFamilyNameKey¶
WWSFamilyName
- GSPropertyNameWWSSubfamilyNameKey¶
WWSSubfamilyName
- GSPropertyNameVariationsPostScriptNamePrefixKey¶
VariationsPostScriptNamePrefix
Added in version 3.1.
Instance Types¶
- INSTANCETYPESINGLE¶
single interpolation instance
- INSTANCETYPEVARIABLE¶
variable font setting
Added in version 3.0.1.
Hint Types¶
- TOPGHOST¶
Top ghost for PS hints
- STEM¶
Stem for PS hints
- BOTTOMGHOST¶
Bottom ghost for PS hints
- TTSNAP¶
Snap for TT hints
- TTSTEM¶
Stem for TT hints
- TTSHIFT¶
Shift for TT hints
- TTINTERPOLATE¶
Interpolation for TT hints
- TTDIAGONAL¶
Diagonal for TT hints
- TTDELTA¶
Delta TT hints
- CORNER¶
Corner Component
path = Layer.shapes[0] brush = GSHint() brush.name = "_corner.test" brush.type = CORNER brush.originNode = path.nodes[1] Layer.hints.append(brush)
- CAP¶
Cap Component
- BRUSH¶
Brush Component
Added in version 3.1.
- SEGMENT¶
Segment Component
Added in version 3.1.
Hint Option¶
This is only used for TrueType hints.
- TTROUND¶
Round to grid
- TTROUNDUP¶
Round up
- TTROUNDDOWN¶
Round down
- TTDONTROUND¶
Don’t round at all
- TRIPLE = 128
Indicates a triple hint group. There need to be exactly three horizontal TTStem hints with this setting to take effect.
Callback Keys¶
This are the available callbacks
- DRAWFOREGROUND¶
to draw in the foreground
- DRAWBACKGROUND¶
to draw in the background
- DRAWINACTIVE¶
draw inactive glyphs
- DOCUMENTOPENED¶
is called if a new document is opened
- DOCUMENTACTIVATED¶
is called when the document becomes the active document
- DOCUMENTWASSAVED¶
is called when the document is saved. The document itself is passed in notification.object()
- DOCUMENTEXPORTED¶
if a font is exported. This is called for every instance and
notification.object()will contain the path to the final font file.def exportCallback(info): try: print(info.object()) except: # Error. Print exception. import traceback print(traceback.format_exc()) # add your function to the hook Glyphs.addCallback(exportCallback, DOCUMENTEXPORTED)
- DOCUMENTCLOSED¶
is called when the document is closed
Deprecated since version 3.0.4: please use DOCUMENTWILLCLOSE
- DOCUMENTWILLCLOSE¶
is called just before a document will be closed
the info object contains the GSWindowController object
Added in version 3.0.4.
- DOCUMENTDIDCLOSE¶
is called after a document was closed
the info object contains the NSDocument object
Added in version 3.0.4.
- TABDIDOPEN¶
if a new tab is opened
- TABWILLCLOSE¶
if a tab is closed
- UPDATEINTERFACE¶
if some thing changed in the edit view. Maybe the selection or the glyph data.
- MOUSEMOVED¶
is called if the mouse is moved. If you need to draw something, you need to call
Glyphs.redraw()and also register to one of the drawing callbacks.
- FILTER_FLAT_KERNING¶
is called when exporting a kern table
In a (general) plugin, implement a method like this:
@objc.typedSelector(b'@@:@o^@') def filterFlatKerning_error_(self, flatKerning, error): newKerning = list() for kern in flatKerning: name1 = kern[0] name2 = kern[1] if len(name1) > 1 and len(name2) > 1: # this is way oversimplified. continue if abs(kern[2]) < 10: # ignore small pairs continue newKerning.append(kern) return newKerning, None
Register the callback like this:
GSCallbackHandler.addCallback_forOperation_(self, FILTER_FLAT_KERNING) # self needs to be a subclass of NSObject (as all plugins are)
Added in version 3.2.
Writing Directions¶
The writing directions of the Edit View.
- GSBIDI¶
for characters that follow the main writing direction (like punctuation)
- GSLTR¶
Left to Right (e.g. Latin)
- GSRTL¶
Right to Left (e.g. Arabic, Hebrew)
- GSVertical¶
Top to Bottom, Right to Left (e.g. Chinese, Japanese, Korean)
- GSVerticalToRight¶
Top to Bottom, Left to Right (e.g. Mongolian)
Shape Type¶
- GSShapeTypePath¶
Path
- GSShapeTypeComponent¶
Component
Annotation Types¶
- TEXT¶
- ARROW¶
- CIRCLE¶
- PLUS¶
- MINUS¶
Inspector Sizes¶
- GSInspectorSizeSmall¶
- GSInspectorSizeRegular¶
- GSInspectorSizeLarge¶
- GSInspectorSizeXLarge¶
Metrics Types¶
metrics types are used in GSFont.metrics. see GSMetric.type
- GSMetricsTypeUndefined¶
- GSMetricsTypeAscender¶
- GSMetricsTypeCapHeight¶
- GSMetricsTypeSlantHeight¶
- GSMetricsTypexHeight¶
- GSMetricsTypeMidHeight¶
- GSMetricsTypeBodyHeight¶
- GSMetricsTypeDescender¶
- GSMetricsTypeBaseline¶
- GSMetricsTypeItalicAngle¶
Component Alignment¶
constant for the GSComponent.alignment property
- GSAlignmentNoAligned¶
- GSAlignmentDisable¶
- GSAlignmentDefault¶
- GSAlignmentForce¶
- GSAlignmentAligned¶
- GSAlignmentHorizontal¶